Alternative Splicing of Human Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase (hTERT) and Its Implications in Physiological and Pathological Processes
- PMID: 34065134
- PMCID: PMC8150890
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines9050526
Alternative Splicing of Human Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase (hTERT) and Its Implications in Physiological and Pathological Processes
Abstract
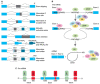
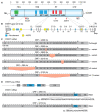
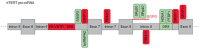
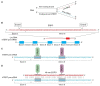
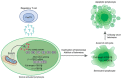
Alternative splicing (AS) of human telomerase catalytic subunit (hTERT, human telomerase reverse transcriptase) pre-mRNA strongly regulates telomerase activity. Several proteins can regulate AS in a cell type-specific manner and determine the functions of cells. In addition to being involved in telomerase activity regulation, AS provides cells with different splice variants that may have alternative biological activities. The modulation of telomerase activity through the induction of hTERT AS is involved in the development of different cancer types and embryos, and the differentiation of stem cells. Regulatory T cells may suppress the proliferation of target human and murine T and B lymphocytes and NK cells in a contact-independent manner involving activation of TERT AS. This review focuses on the mechanism of regulation of hTERT pre-mRNA AS and the involvement of splice variants in physiological and pathological processes.
Keywords: alternative splicing; apoptosis; endonuclease G; human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT); lymphocytes; splice variants; telomerase; telomeres.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

