Association between Tobacco Consumption and Problematic Internet Use and the Practice of Physical Activity in Spanish Adolescents
- PMID: 34065308
- PMCID: PMC8161240
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18105464
Association between Tobacco Consumption and Problematic Internet Use and the Practice of Physical Activity in Spanish Adolescents
Abstract
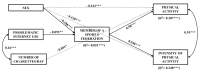
The practice of physical activity (PA) is a healthy habit that offers health benefits. In contrast, the lack thereof may be associated with an increase in diseases, even at an early age. The objective of this study was to analyze the association between unhealthy behaviors, such as tobacco consumption and problematic internet use, and the practice of PA in adolescents. Protective factors (physical activity and sport) and risk factors (leading a sedentary life, tobacco use, and problematic internet use) were evaluated. Other variables such as sex, the intensity of physical activity, and being a member of a sports federation were also evaluated. The sample consisted of a total of 1222 Spanish adolescents. Univariate descriptive analysis and multiple linear regression were used, and confirmatory factor analyses and structural models were also estimated. The results confirm a significant positive association between physical activity, intensity, and being a member of a sports federation, as well as between cigarette consumption and internet use. It is advisable to implement public policies that promote the practice of sports as a direct investment in health, preventing the consumption of tobacco and other habits that are harmful to the health of adolescents.
Keywords: adolescence; health; internet; physical activity; sports federation; tobacco.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Relationship between tobacco consumption and physical exercise in adolescents. Differences between genders].Adicciones. 2013;25(1):29-36. Adicciones. 2013. PMID: 23487277 Spanish.
-
Physical exercise, energy expenditure and tobacco consumption in adolescents from Murcia (Spain).Arch Argent Pediatr. 2014 Feb;112(1):12-8. doi: 10.5546/aap.2014.eng.12. Arch Argent Pediatr. 2014. PMID: 24566776 English, Spanish.
-
Physical Activity and Snus: Is There a Link?Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2015 Jun 25;12(7):7185-98. doi: 10.3390/ijerph120707185. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2015. PMID: 26121189 Free PMC article.
-
[Relationship between tobacco consumption and sport practice among health and education science university students].Enferm Clin. 2017 Jan-Feb;27(1):21-27. doi: 10.1016/j.enfcli.2016.08.008. Epub 2016 Nov 3. Enferm Clin. 2017. PMID: 27817984 Spanish.
-
[Alcohol and tobacco consumption in Spanish and Mexican adolescents and its relation to physical and sports-related activity and to the family].Rev Panam Salud Publica. 2012 Mar;31(3):211-20. doi: 10.1590/s1020-49892012000300005. Rev Panam Salud Publica. 2012. PMID: 22569695 Spanish.
Cited by
-
Alcohol, Tobacco and Cannabis Consumption on Physical Activity and Physical and Social Self-Concept in Secondary School Students: An Explanatory Model Regarding Gender.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Aug 18;19(16):10243. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191610243. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36011878 Free PMC article.
-
Problematic Use of the Internet and Cybervictimization: An Empirical Study with Spanish Adolescents.Behav Sci (Basel). 2025 Jun 13;15(6):810. doi: 10.3390/bs15060810. Behav Sci (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40564593 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between physical activity and Internet addiction among Chinese adolescents: exploring latent profile analysis and multi-level mediating mechanisms.Front Psychol. 2025 Jul 9;16:1628586. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1628586. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40703722 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Teesson M., Newton N.C., Slade T., Chapman C., Birrell L., Mewton L., Mather M., Hides L., McBride N., Allsop S., et al. Combined prevention for substance use, depression, and anxiety in adolescence: A cluster-randomised controlled trial of a digital online intervention. Lancet Digit. Health. 2020;2:e74–e84. doi: 10.1016/S2589-7500(19)30213-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Physical Activity Guidelines Advisory Committee Report. [(accessed on 17 March 2021)];2008 Available online: http://www.europarc.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/Physical-Activity-Gui....
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

