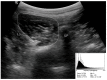
Ultrasound Imaging Analysis of the Lumbar Multifidus Muscle Echo Intensity: Intra-Rater and Inter-Rater Reliability of a Novice and an Experienced Rater
- PMID: 34065340
- PMCID: PMC8160687
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina57050512
Ultrasound Imaging Analysis of the Lumbar Multifidus Muscle Echo Intensity: Intra-Rater and Inter-Rater Reliability of a Novice and an Experienced Rater
Abstract
Background and Objectives: Ultrasound echo intensity (EI) of the lumbar multifidus muscle (LMM) could offer valuable insights regarding muscle quality in people with low back pain (LBP). However, whether the rater's experience noticeably influences the reliability and precision of LMM EI measurements has not been established. The aims of this study were to investigate the intra-rater and inter-rater reliability of LMM EI measurements, and to compare the reliability and SEM between a novice and an experienced rater. Materials and Methods: Twenty athletes (10 females, 10 males) with a history of LBP were included in this study. Transverse ultrasound images of LMM were taken at L5 in prone. LMM EI measurements were obtained bilaterally by tracing the maximum ROI representing the LMM cross-sectional area (CSA), avoiding the inclusion of bone or surrounding fascia. All measurements were performed by two novice raters and an experienced researcher. Each measurement was acquired by each rater three times for each side on three different images, and the average was used in the analyses. Raters were blinded to each other's measurements and the participant's clinical information. Intra-class correlation coefficients (ICCs) were obtained to assess the intra-rater and inter-rater reliability. Results: The intra-rater ICC values for the LMM measurements for the experienced rater were excellent (ICC all > 0.997). The inter-rater reliability ICC values showed moderate to excellent reliability (0.614 to 0.994) and agreement between the novice raters and the experienced rater, except for Novice 1 for the right LMM, which revealed lower ICCs and a wider 95% CI. Intra-rater and inter-rater reliability results were similar when separately looking at the right and left side of the muscle and participant gender. Conclusions: Our findings support the clinical use of ultrasound imaging for the assessment of LMM EI in individuals with LBP.
Keywords: echo intensity; low back pain; multifidus muscle; reliability; ultrasound imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intra-rater and inter-rater reliability of rehabilitative ultrasound imaging of cervical multifidus muscle in healthy people: Imaging capturing and imaging calculation.Musculoskelet Sci Pract. 2020 Aug;48:102158. doi: 10.1016/j.msksp.2020.102158. Epub 2020 Mar 20. Musculoskelet Sci Pract. 2020. PMID: 32217305
-
The effect of low back pain and lower limb injury on lumbar multifidus muscle morphology and function in university soccer players.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020 Feb 12;21(1):96. doi: 10.1186/s12891-020-3119-6. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020. PMID: 32050966 Free PMC article.
-
Measuring ultrasound images of abdominal and lumbar multifidus muscles in older adults: A reliability study.Man Ther. 2016 Jun;23:114-9. doi: 10.1016/j.math.2016.01.004. Epub 2016 Jan 18. Man Ther. 2016. PMID: 26832788
-
Reliability of Real-time Ultrasound Imaging for the Assessment of Trunk Stabilizer Muscles: A Systematic Review of the Literature.J Ultrasound Med. 2019 Jan;38(1):15-26. doi: 10.1002/jum.14661. Epub 2018 Apr 24. J Ultrasound Med. 2019. PMID: 29688574
-
The reliability of video fluoroscopy, ultrasound imaging, magnetic resonance imaging and radiography for measurements of lumbar spine segmental range of motion in-vivo: A review.J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2023;36(1):117-135. doi: 10.3233/BMR-210285. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2023. PMID: 35988213 Review.
Cited by
-
Correlation between Body Composition and Inter-Examiner Errors for Assessing Lumbar Multifidus Muscle Size, Shape and Quality Metrics with Ultrasound Imaging.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Jan 18;10(2):133. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10020133. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36829627 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Virtual Reality Exercises versus Isokinetic Exercises in comparison with Conventional Exercises on the Imaging Findings and Inflammatory Biomarker Changes in Soccer Players with Non-Specific Low Back Pain: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Dec 28;20(1):524. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20010524. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36612846 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Reliability of Panoramic Ultrasound in Assessing Rectus Femoris Size, Shape, and Brightness: An Inter-Examiner Study.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Jan 15;11(1):82. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11010082. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38247959 Free PMC article.
-
Examiner experience moderates reliability of human lower extremity muscle ultrasound measurement - a double blinded measurement error study.Ultrasound J. 2025 Mar 26;17(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s13089-025-00424-6. Ultrasound J. 2025. PMID: 40138073 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kay A.G. An extensive literature review of the lumbar multifidus: Biomechanics. J. Man. Manip. Ther. 2001;9:17–39. doi: 10.1179/jmt.2001.9.1.17. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous