Mechanisms of TP53 Pathway Inactivation in Embryonic and Somatic Cells-Relevance for Understanding (Germ Cell) Tumorigenesis
- PMID: 34065345
- PMCID: PMC8161298
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22105377
Mechanisms of TP53 Pathway Inactivation in Embryonic and Somatic Cells-Relevance for Understanding (Germ Cell) Tumorigenesis
Abstract
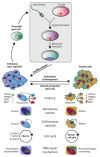
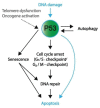
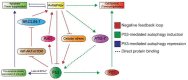
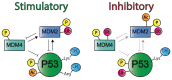
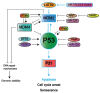
The P53 pathway is the most important cellular pathway to maintain genomic and cellular integrity, both in embryonic and non-embryonic cells. Stress signals induce its activation, initiating autophagy or cell cycle arrest to enable DNA repair. The persistence of these signals causes either senescence or apoptosis. Over 50% of all solid tumors harbor mutations in TP53 that inactivate the pathway. The remaining cancers are suggested to harbor mutations in genes that regulate the P53 pathway such as its inhibitors Mouse Double Minute 2 and 4 (MDM2 and MDM4, respectively). Many reviews have already been dedicated to P53, MDM2, and MDM4, while this review additionally focuses on the other factors that can deregulate P53 signaling. We discuss that P14ARF (ARF) functions as a negative regulator of MDM2, explaining the frequent loss of ARF detected in cancers. The long non-coding RNA Antisense Non-coding RNA in the INK4 Locus (ANRIL) is encoded on the same locus as ARF, inhibiting ARF expression, thus contributing to the process of tumorigenesis. Mutations in tripartite motif (TRIM) proteins deregulate P53 signaling through their ubiquitin ligase activity. Several microRNAs (miRNAs) inactivate the P53 pathway through inhibition of translation. CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF) maintains an open chromatin structure at the TP53 locus, explaining its inactivation of CTCF during tumorigenesis. P21, a downstream effector of P53, has been found to be deregulated in different tumor types. This review provides a comprehensive overview of these factors that are known to deregulate the P53 pathway in both somatic and embryonic cells, as well as their malignant counterparts (i.e., somatic and germ cell tumors). It provides insights into which aspects still need to be unraveled to grasp their contribution to tumorigenesis, putatively leading to novel targets for effective cancer therapies.
Keywords: P53 pathway; cancers; embryonic and somatic cells; mutations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Low p14ARF expression in neuroblastoma cells is associated with repressed histone mark status, and enforced expression induces growth arrest and apoptosis.Hum Mol Genet. 2013 May 1;22(9):1735-45. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt020. Epub 2013 Jan 23. Hum Mol Genet. 2013. PMID: 23343716
-
Resistance mechanisms to TP53-MDM2 inhibition identified by in vivo piggyBac transposon mutagenesis screen in an Arf-/- mouse model.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Mar 21;114(12):3151-3156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1620262114. Epub 2017 Mar 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28265066 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation of TP53 and alteration of p14(arf) expression in EGFR- and KRAS-mutated lung adenocarcinomas.Clin Lung Cancer. 2014 Mar;15(2):124-30. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2013.08.003. Epub 2013 Oct 26. Clin Lung Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24169260
-
Transcription factors that interact with p53 and Mdm2.Int J Cancer. 2016 Apr 1;138(7):1577-85. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29663. Epub 2015 Jul 14. Int J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26132471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-Translational Regulation of ARF: Perspective in Cancer.Biomolecules. 2020 Aug 4;10(8):1143. doi: 10.3390/biom10081143. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32759846 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of TP53 in Cisplatin Resistance in Mediastinal and Testicular Germ Cell Tumors.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 29;22(21):11774. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111774. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769213 Free PMC article.
-
KP772 overcomes multiple drug resistance in malignant lymphoma and leukemia cells in vitro by inducing Bcl-2-independent apoptosis and upregulation of Harakiri.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2021 Dec;26(8):897-907. doi: 10.1007/s00775-021-01900-9. Epub 2021 Oct 6. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2021. PMID: 34617137 Free PMC article.
-
Caprylic Acid (FFA C8:0) promotes the progression of prostate cancer by up-regulating G protein-coupled receptor 84/ Krüppel-like factor 7.BMC Cancer. 2023 May 11;23(1):426. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-10841-2. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37170248 Free PMC article.
-
Depletion of TP53 in Human Pluripotent Stem Cells Triggers Malignant-Like Behavior.Adv Biol (Weinh). 2025 Apr;9(4):e2400538. doi: 10.1002/adbi.202400538. Epub 2025 Jan 6. Adv Biol (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39760438 Free PMC article.
-
MI-773, a breaker of the MDM2/p53 axis, exhibits anticancer effects in neuroblastoma via downregulation of INSM1.Oncol Lett. 2021 Dec;22(6):838. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.13099. Epub 2021 Oct 18. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 34712362 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

