Synergistic Effects of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Bacteria Reduce Heavy Metals Toxicity in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Plant
- PMID: 34065355
- PMCID: PMC8160611
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics9050113
Synergistic Effects of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Bacteria Reduce Heavy Metals Toxicity in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Plant
Abstract
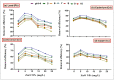
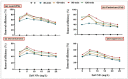
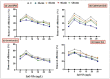
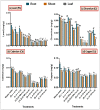
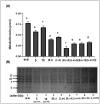
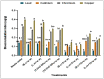
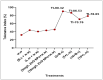
Heavy metals (HMs) are toxic elements which contaminate the water bodies in developing countries because of their excessive discharge from industrial zones. Rice (Oryza sativa L) crops are submerged for a longer period of time in water, so irrigation with HMs polluted water possesses toxic effects on plant growth. This study was initiated to observe the synergistic effect of bacteria (Bacillus cereus and Lysinibacillus macroides) and zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) (5, 10, 15, 20 and 25 mg/L) on the rice that were grown in HMs contaminated water. Current findings have revealed that bacteria, along with ZnO NPs at lower concentration, showed maximum removal of HMs from polluted water at pH 8 (90 min) as compared with higher concentrations. Seeds primed with bacteria grown in HM polluted water containing ZnO NPs (5 mg/L) showed reduced uptake of HMs in root, shoot and leaf, thus resulting in increased plant growth. Furthermore, their combined effects also reduced the bioaccumulation index and metallothionine (MTs) content and enhanced the tolerance index of plants. This study suggested that synergistic treatment of bacteria with lower concentrations of ZnO NPs helped plants to reduce heavy metal toxicity, especially Pb and Cu, and enhanced plant growth.
Keywords: bacteria; heavy metals; nanoparticles; polluted water; synergistic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Combine Effect of ZnO NPs and Bacteria on Protein and Gene's Expression Profile of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Plant.Toxics. 2022 Jun 3;10(6):305. doi: 10.3390/toxics10060305. Toxics. 2022. PMID: 35736913 Free PMC article.
-
Multifaceted roles of zinc nanoparticles in alleviating heavy metal toxicity in plants: a comprehensive review and future perspectives.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024 Nov;31(52):61356-61376. doi: 10.1007/s11356-024-35018-7. Epub 2024 Oct 19. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024. PMID: 39424645 Review.
-
Impact of ZnO nanoparticles on Cd toxicity and bioaccumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.).Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019 Aug;26(22):23119-23128. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-05551-x. Epub 2019 Jun 11. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31183760
-
Combined use of biochar and zinc oxide nanoparticle foliar spray improved the plant growth and decreased the cadmium accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) plant.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019 Apr;26(11):11288-11299. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-04554-y. Epub 2019 Feb 22. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019. PMID: 30793248
-
Promises and potential of in situ nano-phytoremediation strategy to mycorrhizo-remediate heavy metal contaminated soils using non-food bioenergy crops (Vetiver zizinoides & Cannabis sativa).Int J Phytoremediation. 2020;22(9):900-915. doi: 10.1080/15226514.2020.1774504. Epub 2020 Jun 13. Int J Phytoremediation. 2020. PMID: 32538143 Review.
Cited by
-
Biosynthesis and Mathematical Interpretation of Zero-Valent Iron NPs Using Nigella sativa Seed Tincture for Indemnification of Carcinogenic Metals Present in Industrial Effluents.Molecules. 2023 Apr 7;28(8):3299. doi: 10.3390/molecules28083299. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37110533 Free PMC article.
-
Bacillus subtilis Synthesized Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (Fe3O4 NPs) Induced Metabolic and Anti-Oxidative Response in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) under Arsenic Stress.Toxics. 2022 Oct 18;10(10):618. doi: 10.3390/toxics10100618. Toxics. 2022. PMID: 36287898 Free PMC article.
-
Reducing lead toxicity with advanced nanotechnology methods.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 24. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04170-3. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40272519 Review.
-
Potential Effects of Metal Oxides on Agricultural Production of Rice: A Mini Review.Plants (Basel). 2023 Feb 9;12(4):778. doi: 10.3390/plants12040778. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36840126 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Improve Pleioblastus pygmaeus Plant Tolerance to Arsenic and Mercury by Stimulating Antioxidant Defense and Reducing the Metal Accumulation and Translocation.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Feb 28;13:841501. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.841501. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35295636 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Azimi A., Azari A., Rezakazemi M., Ansarpour M. Removal of heavy metals from industrial wastewaters: A review. Chem. Biol. Eng. Rev. 2017;4:37–59. doi: 10.1002/cben.201600010. - DOI
-
- Amin N., Ayaz M., Alam S., Gul S. Heavy metals contamination through industrial effluent to irrigation water in GadoonAmazai (Swabi) and Hayatabad (Peshawar) Pakistan. J. Sci. Res. 2013;6:111–124. doi: 10.3329/jsr.v6i1.16336. - DOI
-
- Randhawa M.A., Ahmad G., Anjum F.M., Asghar A., Sajid M.W. Heavy metal contents and their daily intake in vegetables under peri-urban farming system of Multan, Pakistan. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2014;51:1–20.
-
- Bangash F.K., Fida M., Fazeelat T. Appraisal of effluents of some selected industries of Hayatabad industrial estate, Peshawar. J. Chem. Soc. Pak. 2006;28:16–19.
-
- Nawaz A., Khurshid K., Arif M.S., Ranjha A.M. Accumulation of heavy metals in soil and rice plant (Oryza sativa L.) irrigated with industrial effluents. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2006;8:391–393.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

