A Randomized Trial of Tai Chi on Preventing Hypertension and Hyperlipidemia in Middle-Aged and Elderly Patients
- PMID: 34065454
- PMCID: PMC8160700
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18105480
A Randomized Trial of Tai Chi on Preventing Hypertension and Hyperlipidemia in Middle-Aged and Elderly Patients
Abstract
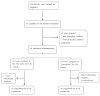
In our randomized controlled trial, we investigated whether Wu-style Tai Chi (Tai Chi combined with Daoyin) as a potential exercise prescription is more effective than simplified Tai Chi in the prevention and treatment of hypertension and hyperlipidemia in the middle-aged and elderly. We randomly assigned 66 patients with hypertension and hyperlipidemia to one of the two groups: the Wu-style Tai Chi group or the simplified Tai Chi group; the simplified Tai Chi group only exercised simplified Tai Chi three times a week for 6 weeks. The Wu-style Tai Chi group participated in 60 min of Wu-style Tai Chi three times a week for 6 weeks. Serum biochemical tests were conducted at baseline and at the end of the study. Measurements of blood pressure were performed at the same time. Primary outcomes were compared within and between groups at baseline and at 6 weeks. The participants in the Wu-style Tai Chi group performed, at 6 weeks, significantly better than baseline on all of the primary outcomes (p value ≤ 0.05). The results also show significant difference within the simplified Tai Chi group from baseline to 6 weeks in TCHO (mmol/L), SBP (mmHg), and LDL-C (mmol/L) (p value < 0.05). From baseline to 6 weeks, the Wu-style Tai Chi group had significant differences at more test indexes in serum and blood pressure than the simplified Tai Chi group. At 6 weeks, the Wu-style Tai Chi group had a significantly greater mean improvement in the SBP (mmHg) than did the simplified Tai Chi group (mean between-group difference, -5.80 (mmHg) [95% CI, -14.01 to 2.41]; p = 0.007). The results showed that, compared with simplified Tai Chi, Wu-style Tai Chi had a better effect on hypertension in the middle-aged and elderly. At 6 weeks in LDL-C (mmol/L), the Wu-style Tai Chi group had significantly greater improvement between the two groups (means between-group difference, -0.45 (mmol/L) [95% CI, -0.89 to -0.17]; p = 0.03). The results showed that Wu-style Tai Chi protected the cardiovascular system of the middle-aged and elderly in improving LDL-C (mmol/L), and was more significant than simplified Tai Chi. After 6 weeks of exercise, Wu-style Tai Chi could effectively improve hyperlipidemia and hypertension. The total effective rate of cardiovascular disease was 90.00%. There was significant difference in the treatment effect of hypertension and hyperlipidemia between the two groups during 6 weeks (p = 0.039), showing that, in a small population of middle-aged and elderly subjects, Wu style Tai Chi could be useful in managing important CV risk factors, such as hypertension and hyperlipidemia.
Keywords: Tai Chi; cardiovascular disease; the middle-aged and elderly.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tai Chi exercise is more effective than brisk walking in reducing cardiovascular disease risk factors among adults with hypertension: A randomised controlled trial.Int J Nurs Stud. 2018 Dec;88:44-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2018.08.009. Epub 2018 Aug 24. Int J Nurs Stud. 2018. PMID: 30195124 Clinical Trial.
-
Meta-analysis of the intervention effects of tai chi on fasting blood glucose, blood pressure and triglyceride in middle-aged and elderly people.Aging Male. 2024 Dec;27(1):2282977. doi: 10.1080/13685538.2023.2282977. Epub 2024 Jan 23. Aging Male. 2024. PMID: 38259166 Review.
-
Impact of a Precision Intervention for Vascular Health in Middle-Aged and Older Postmenopausal Women Using Polar Heart Rate Sensors: A 24-Week RCT Study Based on the New Compilation of Tai Chi (Bafa Wubu).Sensors (Basel). 2024 Sep 8;24(17):5832. doi: 10.3390/s24175832. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39275744 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Tai Chi versus aerobic exercise on blood pressure in prehypertension patients (TCOBPP): a study protocol for a 12-month single-blind randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2022 Dec 12;23(1):1001. doi: 10.1186/s13063-022-06840-6. Trials. 2022. PMID: 36510218 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the different Tai Chi exercise cycles on patients with essential hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Mar 3;10:1016629. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1016629. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 36937925 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of six traditional Chinese mind-body exercises on obesity and cardiovascular risk factors in middle-aged and elderly hypertensive patients: a network Meta-Analysis of 49 RCTs.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025 Aug 18;25(1):606. doi: 10.1186/s12872-025-05084-x. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025. PMID: 40826319
-
Quality of Evidence Supporting the Effects of Tai Chi Exercise on Essential Hypertension: An Overview of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses.Cardiol Res Pract. 2022 Apr 30;2022:4891729. doi: 10.1155/2022/4891729. eCollection 2022. Cardiol Res Pract. 2022. PMID: 35535247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of six Chinese mind-body exercise therapies on glycolipid metabolism and vascular endothelial function in hypertensive patients.iScience. 2025 May 15;28(6):112682. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112682. eCollection 2025 Jun 20. iScience. 2025. PMID: 40510132 Free PMC article.
-
Physical Exercise and Diet: Regulation of Gut Microbiota to Prevent and Treat Metabolic Disorders to Maintain Health.Nutrients. 2023 Mar 22;15(6):1539. doi: 10.3390/nu15061539. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36986268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Tai Chi Softball on Health-Related Outcomes in Elderly Men.Am J Mens Health. 2025 Mar-Apr;19(2):15579883251332745. doi: 10.1177/15579883251332745. Epub 2025 Apr 30. Am J Mens Health. 2025. PMID: 40304406 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- WHO Key Facts. Noncommunicable Diseases. [(accessed on 13 April 2021)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/noncommunicable-diseases.
-
- Zhou M., Wang H., Zeng X., Yin P., Zhu J., Chen W., Li X., Wang L., Wang L., Liu Y., et al. Mortality, morbidity, and risk factors in China and its provinces, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2019;394:1145–1158. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30427-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chinese Society of Geriatrics Hypertension Branch China experts consensus on the managements of hypertension in the very old people. Chin. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2015;20:401–409.
-
- Ference B.A., Ginsberg H.N., Graham I., Ray K.K., Packard C.J., Bruckert E., Hegele R.A., Krauss R.M., Raal F.J., Schunkert H., et al. Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. 1. Evidence from genetic, epidemiologic, and clinical studies. A consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel. Eur. Heart J. 2017;38:2459–2472. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx144. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical