The Evolving Role of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treatment
- PMID: 34065489
- PMCID: PMC8160723
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines9050532
The Evolving Role of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treatment
Abstract
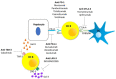
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of most common cancers and the fourth leading cause of death worldwide. Commonly, HCC development occurs in a liver that is severely compromised by chronic injury or inflammation. Liver transplantation, hepatic resection, radiofrequency ablation (RFA), transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE), and targeted therapies based on tyrosine protein kinase inhibitors are the most common treatments. The latter group have been used as the primary choice for a decade. However, tumor microenvironment in HCC is strongly immunosuppressive; thus, new treatment approaches for HCC remain necessary. The great expression of immune checkpoint molecules, such as programmed death-1 (PD-1), cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4), lymphocyte activating gene 3 protein (LAG-3), and mucin domain molecule 3 (TIM-3), on tumor and immune cells and the high levels of immunosuppressive cytokines induce T cell inhibition and represent one of the major mechanisms of HCC immune escape. Recently, immunotherapy based on the use of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), as single agents or in combination with kinase inhibitors, anti-angiogenic drugs, chemotherapeutic agents, and locoregional therapies, offers great promise in the treatment of HCC. This review summarizes the recent clinical studies, as well as ongoing and upcoming trials.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma; immune checkpoint inhibitors; immune checkpoint molecules; immune microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Dimitroulis D., Damaskos C., Valsami S., Davakis S., Garmpis N., Spartalis E., Athanasiou A., Moris D., Sakellariou S., Kykalos S., et al. From diagnosis to treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: An epidemic problem for both developed and developing world. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017;23:5282–5294. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i29.5282. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

