A Randomized Controlled Trial Evaluating Integrative Psychotherapeutic Group Treatment Compared to Self-Help Groups in Functional Vertigo/Dizziness
- PMID: 34065517
- PMCID: PMC8161006
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10102215
A Randomized Controlled Trial Evaluating Integrative Psychotherapeutic Group Treatment Compared to Self-Help Groups in Functional Vertigo/Dizziness
Abstract
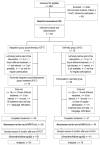
We tested the efficacy of an integrative psychotherapeutic group treatment (IPGT) in reducing vertigo/dizziness-related impairment along with depression, anxiety, and somatization by conducting a randomized controlled superiority trial comparing IPGT to self-help groups moderated by a clinical psychologist (SHG). Adult patients with functional vertigo and dizziness symptoms were randomly allocated to either the IPGT or SHG as active control group. Outcomes were assessed at baseline (t0), after treatment lasting 16 weeks (t1), and 12 months after treatment (t2). A total of 81 patients were assigned to IPGT and 78 patients were assigned to SHG. Vertigo-related impairment was reduced in both conditions (IPGT: t0-t1: d = 1.10, t0-t2: d = 1.06; SHG: t0-t1: d = 0.86, t0-t2: d = 1.29), showing the efficiency of both IPGT and SHG. Clinically relevant improvements were also obtained for depression in both groups. Linear mixed model analyses revealed no differences between groups for all outcomes (effect of group for the primary outcome: b = -1.15, SE = 2.13, t = -0.54, p = 0.59). Attrition rates were higher in SHG (52.6%) than in IPGT (28.4%). Both conditions improved primary and secondary outcomes while IPGT was better accepted by patients than SHG. Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, Identifier: NCT02320851.
Keywords: dizziness; psychotherapy; randomized controlled trial; vertigo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
-
- Grill E., Heuberger M., Strobl R., Saglam M., Holle R., Linkohr B., Ladwig K.-H., Peters A., Schneider E., Jahn K., et al. Prevalence, Determinants, and consequences of vestibular hypofunction. results from the KORA-FF4 survey. Front. Neurol. 2018;9:1076. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.01076. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical