Optimization of Glycerol-Water Extraction of Selected Bioactive Compounds from Peppermint and Common Nettle
- PMID: 34065576
- PMCID: PMC8160696
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox10050817
Optimization of Glycerol-Water Extraction of Selected Bioactive Compounds from Peppermint and Common Nettle
Abstract
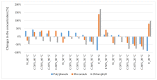
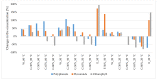
Current trends in the industry indicate that extraction solvents should conform with the ideals of so-called "green chemistry". Therefore, the objective of the presented study was to optimize the conditions for the extraction of polyphenols, flavonoids and chlorophyll from peppermint leaves (Mentha × piperita L., Lamiaceae) and from common nettle leaves (Urtica dioica L., Urticaceae) via green chemistry. The obtained experimental results were subjected to modelling by means of the multiple regression method, while the optimization of the system was addressed via the application of the desirability function. As a result of the use of glycerol-water systems for the extraction of the tested active compounds from mint leaves and nettle leaves, extracts with higher concentrations of polyphenols, flavonoids and chlorophyll were most often obtained, when compared with the use of classical solvents such as water and ethanol. In this work, we demonstrate that the extraction temperature has significant influence on the concentration of the determined components in the extracts. To obtain the highest values of the analysed parameters, leaves of peppermint should be extracted with glycerol-water mixture at the proportions of 30.5:69.5 at a temperature of 50 °C, while the optimal conditions for the extraction of leaves of common nettle were the glycerol-water proportions of 12.5:87.5 and extraction temperature of 20 °C. Comparing the average percentage differences between the highest values of the analysed parameters obtained in the experiment and the approximated values for various temperatures with the level of desirability, one can note a high correlation that, in the analysed examples, amounted to 0.9681. The study showed that glycerol can be an alternative solvent in the extraction of polyphenols, flavonoids and chlorophyll, replacing, e.g., ethanol-which, for various reasons, cannot always be used.
Keywords: chlorophyll; extraction; flavonoids; glycerol; polyphenols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antioxidant Extracts of Nettle (Urtica dioica) Leaves: Evaluation of Extraction Techniques and Solvents.Molecules. 2022 Sep 15;27(18):6015. doi: 10.3390/molecules27186015. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36144748 Free PMC article.
-
Wild Stinging Nettle (Urtica dioica L.) Leaves and Roots Chemical Composition and Phenols Extraction.Plants (Basel). 2023 Jan 9;12(2):309. doi: 10.3390/plants12020309. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36679022 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of Copper and Zinc on Photosynthesis and Phenolic Levels in Basil (Ocimum basilicum L.), Borage (Borago officinalis L.), Common Nettle (Urtica dioica L.) and Peppermint (Mentha piperita L.).Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 23;25(7):3612. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073612. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612424 Free PMC article.
-
Stinging Nettle (Urtica dioica L.): Nutritional Composition, Bioactive Compounds, and Food Functional Properties.Molecules. 2022 Aug 16;27(16):5219. doi: 10.3390/molecules27165219. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36014458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Final report on the safety assessment of Mentha Piperita (Peppermint) Oil, Mentha Piperita (Peppermint) Leaf Extract, Mentha Piperita (Peppermint) Leaf, and Mentha Piperita (Peppermint) Leaf Water.Int J Toxicol. 2001;20 Suppl 3:61-73. Int J Toxicol. 2001. PMID: 11766133 Review.
Cited by
-
Antioxidant Extracts of Nettle (Urtica dioica) Leaves: Evaluation of Extraction Techniques and Solvents.Molecules. 2022 Sep 15;27(18):6015. doi: 10.3390/molecules27186015. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36144748 Free PMC article.
-
Extraction of Isoflavones, Alpha-Hydroxy Acids, and Allantoin from Soybean Leaves-Optimization by a Mixture Design of the Experimental Method.Molecules. 2023 May 8;28(9):3963. doi: 10.3390/molecules28093963. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37175385 Free PMC article.
-
Nettle Leaf Water Extracts for Hepatoprotection: Insights into Bioactivity and Mitochondrial Function.Plants (Basel). 2025 Mar 21;14(7):992. doi: 10.3390/plants14070992. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40219059 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing the Solvent Selection of the Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Sea Buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) Pomace: Phenolic Profiles and Antioxidant Activity.Foods. 2024 Feb 2;13(3):482. doi: 10.3390/foods13030482. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38338617 Free PMC article.
-
A Fresh Look at Mouthwashes-What Is Inside and What Is It For?Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Mar 25;19(7):3926. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19073926. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35409608 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arumugam P., Ramamurthy P., Santhiya S.T., Ramesh A. Antioxidant activity measured in different solvent fractions obtained from Mentha spicata Linn.: An analysis by ABTS.+ decolorization assay. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006;15:119–124. - PubMed
-
- Pinelo M., Rubilar M., Jerez M., Sineiro J., Núñez M.J. Effect of Solvent, Temperature, and Solvent-to-Solid Ratio on the Total Phenolic Content and Antiradical Activity of Extracts from Different Components of Grape Pomace. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005;53:2111–2117. doi: 10.1021/jf0488110. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Spigno G., Tramelli L., De Faveri D.M. Effects of extraction time, temperature and solvent on concentration and antioxidant activity of grape marc phenolics. J. Food Eng. 2007;81:200–208. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2006.10.021. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

