Curcumin at Low Doses Potentiates and at High Doses Inhibits ABT-737-Induced Platelet Apoptosis
- PMID: 34065600
- PMCID: PMC8161296
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22105405
Curcumin at Low Doses Potentiates and at High Doses Inhibits ABT-737-Induced Platelet Apoptosis
Abstract
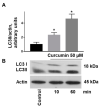
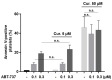
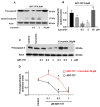
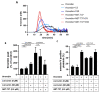
Curcumin is a natural bioactive component derived from the turmeric plant Curcuma longa, which exhibits a range of beneficial activities on human cells. Previously, an inhibitory effect of curcumin on platelets was demonstrated. However, it is unknown whether this inhibitory effect is due to platelet apoptosis or procoagulant platelet formation. In this study, curcumin did not activate caspase 3-dependent apoptosis of human platelets, but rather induced the formation of procoagulant platelets. Interestingly, curcumin at low concentration (5 µM) potentiated, and at high concentration (50 µM) inhibited ABT-737-induced platelet apoptosis, which was accompanied by inhibition of ABT-737-mediated thrombin generation. Platelet viability was not affected by curcumin at low concentration and was reduced by 17% at high concentration. Furthermore, curcumin-induced autophagy in human platelets via increased translocation of LC3I to LC3II, which was associated with activation of adenosine monophosphate (AMP) kinase and inhibition of protein kinase B activity. Because curcumin inhibits P-glycoprotein (P-gp) in cancer cells and contributes to overcoming multidrug resistance, we showed that curcumin similarly inhibited platelet P-gp activity. Our results revealed that the platelet inhibitory effect of curcumin is mediated by complex processes, including procoagulant platelet formation. Thus, curcumin may protect against or enhance caspase-dependent apoptosis in platelets under certain conditions.
Keywords: apoptosis; autophagy; platelets; procoagulant activity; thrombin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

