Sensitive High-Throughput Assays for Tumour Burden Reveal the Response of a Drosophila melanogaster Model of Colorectal Cancer to Standard Chemotherapies
- PMID: 34065887
- PMCID: PMC8151205
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22105101
Sensitive High-Throughput Assays for Tumour Burden Reveal the Response of a Drosophila melanogaster Model of Colorectal Cancer to Standard Chemotherapies
Abstract
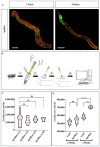
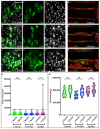
Drosophila melanogaster (Drosophila) models of cancer are emerging as powerful tools to investigate the basic mechanisms underlying tumour progression and identify novel therapeutics. Rapid and inexpensive, it is possible to carry out genetic and drug screens at a far larger scale than in vertebrate organisms. Such whole-organism-based drug screens permits assessment of drug absorption and toxicity, reducing the possibility of false positives. Activating mutations in the Wnt and Ras signalling pathways are common in many epithelial cancers, and when driven in the adult Drosophila midgut, it induces aggressive intestinal tumour-like outgrowths that recapitulate many aspects of human colorectal cancer (CRC). Here we have taken a Drosophila CRC model in which tumourous cells are marked with both GFP and luciferase reporter genes, and developed novel high-throughput assays for quantifying tumour burden. Leveraging these assays, we find that the Drosophila CRC model responds rapidly to treatment with standard CRC-drugs, opening the door to future rapid genetic and drug screens.
Keywords: Drosophila; colorectal cancer; drug screening; high-throughput.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- World Cancer Report: Cander Research for Cancer Prevention. International Agency for Research on Cancer; Lyon, France: 2020.
-
- Rowehl R.A., Burke S., Bialkowska A.B., Pettet D.W., 3rd, Rowehl L., Li E., Antoniou E., Zhang Y., Bergamaschi R., Shroyer K.R., et al. Establishment of highly tumorigenic human colorectal cancer cell line (CR4) with properties of putative cancer stem cells. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e99091. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099091. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

