Biogenic ZnO Nanoparticles Synthesized Using a Novel Plant Extract: Application to Enhance Physiological and Biochemical Traits in Maize
- PMID: 34065934
- PMCID: PMC8151215
- DOI: 10.3390/nano11051270
Biogenic ZnO Nanoparticles Synthesized Using a Novel Plant Extract: Application to Enhance Physiological and Biochemical Traits in Maize
Abstract
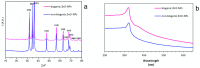
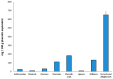
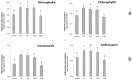
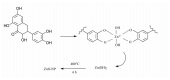
The need to increase crop productivity and resistance directs interest in nanotechnology. Indeed, biogenic metal oxide nanoparticles can promote beneficial effects in plants, while their synthesis avoids the environmental impacts of conventional synthetic procedures. In this context, this research aimed to synthesize biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) using, for the first time, an extract of a wild and spontaneous aquatic species, Lemna minor (duckweed). The effectiveness of this biogenic synthesis was evidenced for comparison with non-biogenic ZnO-NPs (obtained without using the plant extract), which have been synthesized in this research. XRD (X-ray diffraction), FE-SEM (field emission gun electron scanning microscopy), EDX (energy dispersive x-ray spectroscopy), TEM (transmission electron microscope) and UV-vis (ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry) showed the biogenic approach effectiveness. The duckweed extract was subjected to UHPLC-ESI/QTOF-MS (ultra high-pressure liquid chromatography quadrupole time of flight mass spectrometry) phenolic profiling. This untargeted characterization highlighted a high and chemically diverse content in the duckweed extract of compounds potentially implicated in nanoparticulation. From an application standpoint, the effect of biogenic nanoparticles was investigated on some traits of maize subjected to seed priming with a wide range of biogenic ZnO-NPs concentrations. Inductive effects on the shoot and root biomass development were ascertained concerning the applied dosage. Furthermore, the biogenic ZnO-NPs stimulated the content of chlorophylls, carotenoids, and anthocyanin. Finally, the study of malondialdehyde content (MDA) as a marker of the oxidative status further highlighted the beneficial and positive action of the biogenic ZnO-NPs on maize.
Keywords: antioxidant activity; biogenic nanoparticles; duckweed; phytochemicals; plant stimulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Enhancing tomato plant growth in a saline environment through the eco-friendly synthesis and optimization of nanoparticles derived from halophytic sources.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023 Dec;30(56):118830-118854. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-30626-1. Epub 2023 Nov 3. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023. PMID: 37922085
-
Evaluation of the cytotoxicity, antioxidant activity, and molecular docking of biogenic zinc oxide nanoparticles derived from pumpkin seeds.Microsc Res Tech. 2024 Mar;87(3):602-615. doi: 10.1002/jemt.24437. Epub 2023 Nov 28. Microsc Res Tech. 2024. PMID: 38018343
-
Biosynthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activities of zinc oxide nanoparticles from leaf extract of Mentha pulegium (L.).Microb Pathog. 2019 Jun;131:239-245. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2019.04.022. Epub 2019 Apr 17. Microb Pathog. 2019. PMID: 31002961
-
Zinc oxide and zinc oxide-based nanostructures: biogenic and phytogenic synthesis, properties and applications.Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2021 Jul;44(7):1333-1372. doi: 10.1007/s00449-021-02530-w. Epub 2021 Mar 4. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2021. PMID: 33661388 Review.
-
Biogenic nanoparticles: pioneering a new era in breast cancer therapeutics-a comprehensive review.Discov Nano. 2024 Aug 3;19(1):121. doi: 10.1186/s11671-024-04072-y. Discov Nano. 2024. PMID: 39096427 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biosynthesis and Response of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles against Periimplantitis Triggering Pathogens.Materials (Basel). 2022 Apr 27;15(9):3170. doi: 10.3390/ma15093170. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35591502 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and characterization of nano-micronutrient fertilizer and its effect on nutrient availability and maize (Zea Mays L.) productivity in calcareous soils.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 16;15(1):25838. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-11273-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40670602 Free PMC article.
-
Multifunctional ZnO Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Spirodela polyrhiza Extract: Characterization, Photocatalytic Activity, Antimicrobial Assessment, and In Silico Modeling.Bioinorg Chem Appl. 2025 Jul 14;2025:5541535. doi: 10.1155/bca/5541535. eCollection 2025. Bioinorg Chem Appl. 2025. PMID: 40693045 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of Sustainable Use of Biogenic Nanoscale Agro-Materials to Enhance Stress Tolerance and Nutritional Value of Plants.Plants (Basel). 2023 Feb 11;12(4):815. doi: 10.3390/plants12040815. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36840163 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review on the Delivery of Plant-Based Antidiabetic Agents Using Nanocarriers: Current Status and Their Role in Combatting Hyperglycaemia.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Jul 24;14(15):2991. doi: 10.3390/polym14152991. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35893954 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Matussin S., Harunsani M.H., Tan A.L., Khan M.M. Plant-Extract-Mediated SnO2 Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Applications. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020;8:3040–3054. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b06398. - DOI
-
- Kasivelu G., Selvaraj T., Malaichamy K., Kathickeyan D., Shkolnik D., Chaturvedi S. Nano-Micronutrients [γ-Fe2O3(Iron) and ZnO (Zinc)]: Green Preparation, Characterization, Agro-Morphological Characteristics and Crop Productivity Studies in Two Crops (Rice and Maize) New J. Chem. 2020;44:11373–11383. doi: 10.1039/D0NJ02634D. - DOI
-
- Bilesky-José N., Maruyama C., Germano-Costa T., Campos E., Carvalho L., Grillo R., Fraceto L.F., De Lima R. Biogenic α-Fe2O3 Nanoparticles Enhance the Biological Activity of Trichoderma against the Plant Pathogen Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021;9:1669–1683. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c07349. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

