Interrupted Time Series Analysis of Changes in Zolpidem Use Due to Media Broadcasts
- PMID: 34065935
- PMCID: PMC8150593
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18105114
Interrupted Time Series Analysis of Changes in Zolpidem Use Due to Media Broadcasts
Abstract
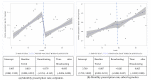
Media has become a major source of information on health and plays a role in the decision-making process on health topics. We aimed to evaluate the association between zolpidem use and media broadcasts that reported the suicide risk. We obtained the data of adult outpatients who have been prescribed zolpidem or other hypnotics from the National Patient Sample database (2015-2017). We evaluated the change in zolpidem or other hypnotic prescription trends based on the prescription rate and average daily prescribed dose before and after July 2016, using interrupted time series analysis. A total of 129,787 adult patients had at least one zolpidem prescription in 3 years. The prescription rate of zolpidem after the broadcast decreased significantly by 0.178% (95% confidence interval (CI): -0.214, -0.142), whereas that of other hypnotic users did not differ from that before the broadcast (-0.020%, 95% CI: -0.088, 0.047). However, the trends in the prescription rate before and after the broadcast did not differ for zolpidem and other hypnotics. Broadcasting medication safety through major public media could have an effect on medication use. After broadcasting about the suicide risk of zolpidem, its overall prescription rate decreased immediately, but the trend was not changed.
Keywords: broadcast; interrupted time series analysis; medication safety; zolpidem.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of Secured Prescription Implementation for Zolpidem on Hypnotics Use in France: A Time-Series Analysis on National Data.Ann Fam Med. 2020 Jul;18(4):345-348. doi: 10.1370/afm.2556. Ann Fam Med. 2020. PMID: 32661036 Free PMC article.
-
Trend changes of national zolpidem users and exposure cases after FDA drug safety communications.Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2021 Nov;30(11):1551-1559. doi: 10.1002/pds.5344. Epub 2021 Aug 23. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2021. PMID: 34382718
-
Correlates of dependence and beliefs about the use of hypnotics among zolpidem and zopiclone users.Subst Use Misuse. 2015 Feb;50(3):350-7. doi: 10.3109/10826084.2014.980955. Epub 2014 Dec 2. Subst Use Misuse. 2015. PMID: 25458710
-
Zolpidem and traffic safety - the importance of treatment compliance.Curr Drug Saf. 2007 Sep;2(3):220-6. doi: 10.2174/157488607781668882. Curr Drug Saf. 2007. PMID: 18690971 Review.
-
Central nervous system side effects associated with zolpidem treatment.Clin Neuropharmacol. 2000 Jan-Feb;23(1):54-8. doi: 10.1097/00002826-200001000-00011. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10682233 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of COVID-19 on resuscitation after hospital arrival for patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: An interrupted time series analysis.Acute Med Surg. 2025 Jan 24;12(1):e70039. doi: 10.1002/ams2.70039. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. Acute Med Surg. 2025. PMID: 39866508 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Qaseem A., Kansagara D., Forciea M.A., Cooke M., Denberg T.D. For the Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians Management of Chronic Insomnia Disorder in Adults: A Clinical Practice Guideline From the American College of Physicians. Ann. Intern. Med. 2016;165:125–133. doi: 10.7326/M15-2175. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources