Assessment of Body Composition in Athletes: A Narrative Review of Available Methods with Special Reference to Quantitative and Qualitative Bioimpedance Analysis
- PMID: 34065984
- PMCID: PMC8150618
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13051620
Assessment of Body Composition in Athletes: A Narrative Review of Available Methods with Special Reference to Quantitative and Qualitative Bioimpedance Analysis
Abstract
Body composition is acknowledged as a determinant of athletic health and performance. Its assessment is crucial in evaluating the efficiency of a diet or aspects related to the nutritional status of the athlete. Despite the methods traditionally used to assess body composition, bioelectric impedance analysis (BIA) and bioelectric impedance vector analysis (BIVA) have recently gained attention in sports, as well as in a research context. Only until recently have specific regression equations and reference tolerance ellipses for athletes become available, while specific recommendations for measurement procedures still remain scarce. Therefore, the present narrative review summarizes the current literature regarding body composition analysis, with a special focus on BIA and BIVA. The use of specific technologies and sampling frequencies is described, and recommendations for the assessment of body composition in athletes are provided. Additionally, the estimation of body composition parameters (i.e., quantitative analysis) and the interpretation of the raw bioelectrical data (i.e., qualitative analysis) are examined, highlighting the innovations now available in athletes. Lastly, it should be noted that, up until 2020, the use of BIA and BIVA in athletes failed to provide accurate results due to unspecific equations and references; however, new perspectives are now unfolding for researchers and practitioners. In light of this, BIA and especially BIVA can be utilized to monitor the nutritional status and the seasonal changes in body composition in athletes, as well as provide accurate within- and between-athlete comparisons.
Keywords: BIVA; bioelectric impedance vector analysis; hydration; localized BIA; nutritional status; phase angle; segmental bioimpedance; tolerance ellipses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
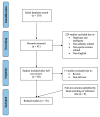
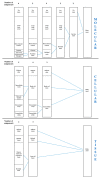





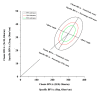
References
-
- Ackland T.R., Lohman T.G., Sundgot-Borgen J., Maughan R.J., Meyer N.L., Stewart A.D., Müller W. Current status of body composition assessment in sport: Review and position statement on behalf of the ad hoc research working group on body composition health and performance, under the auspices of the I.O.C. Medical Commission. Sports Med. 2012;42:227–249. doi: 10.2165/11597140-000000000-00000. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Saltzman E., Mogensen K.M. Nutrition in the Prevention and Treatment of Disease. Elsevier Inc.; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2013. Physical and clinical assessment of nutrition status; pp. 65–79.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

