Correcting for Naturally Occurring Mass Isotopologue Abundances in Stable-Isotope Tracing Experiments with PolyMID
- PMID: 34066041
- PMCID: PMC8151723
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo11050310
Correcting for Naturally Occurring Mass Isotopologue Abundances in Stable-Isotope Tracing Experiments with PolyMID
Abstract
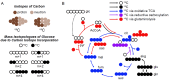
Stable-isotope tracing is a method to measure intracellular metabolic pathway utilization by feeding a cellular system a stable-isotope-labeled tracer nutrient. The power of the method to resolve differential pathway utilization is derived from the enrichment of metabolites in heavy isotopes that are synthesized from the tracer nutrient. However, the readout is complicated by the presence of naturally occurring heavy isotopes that are not derived from the tracer nutrient. Herein we present an algorithm, and a tool that applies it (PolyMID-Correct, part of the PolyMID software package), to computationally remove the influence of naturally occurring heavy isotopes. The algorithm is applicable to stable-isotope tracing data collected on low- and high- mass resolution mass spectrometers. PolyMID-Correct is open source and available under an MIT license.
Keywords: correction; mass isotopologue distribution; metabolic flux analysis; metabolism; natural abundances; stable-isotope tracing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Rosman K.J.R., Taylor P.D.P. Isotopic Compositions of the Elements 1997. Pure Appl. Chem. 1998;70:217–235. doi: 10.1351/pac199870010217. - DOI
-
- Heinrich P., Kohler C., Ellmann L., Kuerner P., Spang R., Oefner P.J., Dettmer K. Correcting for natural isotope abundance and tracer impurity in MS-, MS/MS- and high-resolution-multiple-tracer-data from stable isotope labeling experiments with IsoCorrectoR. Sci. Rep. 2018;8:17910. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-36293-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

