SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Antigen Testing of Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Individuals on the University of Arizona Campus
- PMID: 34066047
- PMCID: PMC8150898
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines9050539
SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Antigen Testing of Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Individuals on the University of Arizona Campus
Abstract
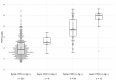
SARS-CoV-2, the cause of COVID19, has caused a pandemic that has infected more than 80 M and killed more than 1.6 M persons worldwide. In the US as of December 2020, it has infected more than 32 M people while causing more than 570,000 deaths. As the pandemic persists, there has been a public demand to reopen schools and university campuses. To consider these demands, it is necessary to rapidly identify those individuals infected with the virus and isolate them so that disease transmission can be stopped. In the present study, we examined the sensitivity of the Quidel Rapid Antigen test for use in screening both symptomatic and asymptomatic individuals at the University of Arizona from June to August 2020. A total of 885 symptomatic and 1551 asymptomatic subjects were assessed by antigen testing and real-time PCR testing. The sensitivity of the test for both symptomatic and asymptomatic persons was between 82 and 90%, with some caveats.
Keywords: PCR; SARS-CoV-2; asymptomatic; diagnostic screening; rapid antigen test.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. [(accessed on 1 February 2021)]; Available online: www.COVID19.who.int.
-
- HCP Fact Sheet. [(accessed on 1 February 2021)]; Available online: www.fda.gov/media/137884/download.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

