The Effect of Calcium-Silicate Cements on Reparative Dentinogenesis Following Direct Pulp Capping on Animal Models
- PMID: 34066444
- PMCID: PMC8125639
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26092725
The Effect of Calcium-Silicate Cements on Reparative Dentinogenesis Following Direct Pulp Capping on Animal Models
Abstract
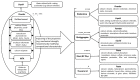
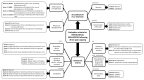
Dental pulp vitality is a desideratum for preserving the health and functionality of the tooth. In certain clinical situations that lead to pulp exposure, bioactive agents are used in direct pulp-capping procedures to stimulate the dentin-pulp complex and activate reparative dentinogenesis. Hydraulic calcium-silicate cements, derived from Portland cement, can induce the formation of a new dentin bridge at the interface between the biomaterial and the dental pulp. Odontoblasts are molecularly activated, and, if necessary, undifferentiated stem cells in the dental pulp can differentiate into odontoblasts. An extensive review of literature was conducted on MedLine/PubMed database to evaluate the histological outcomes of direct pulp capping with hydraulic calcium-silicate cements performed on animal models. Overall, irrespective of their physico-chemical properties and the molecular mechanisms involved in pulp healing, the effects of cements on tertiary dentin formation and pulp vitality preservation were positive. Histological examinations showed different degrees of dental pulp inflammatory response and complete/incomplete dentin bridge formation during the pulp healing process at different follow-up periods. Calcium silicate materials have the ability to induce reparative dentinogenesis when applied over exposed pulps, with different behaviors, as related to the animal model used, pulpal inflammatory responses, and quality of dentin bridges.
Keywords: biomaterials; calcium-silicate cements; dental pulp; dentin bridge; direct pulp capping.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

