Combined Effect of Impregnation with an Origanum vulgare Infusion and Osmotic Treatment on the Shelf Life and Quality of Chilled Chicken Fillets
- PMID: 34066449
- PMCID: PMC8124957
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26092727
Combined Effect of Impregnation with an Origanum vulgare Infusion and Osmotic Treatment on the Shelf Life and Quality of Chilled Chicken Fillets
Abstract
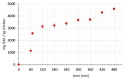
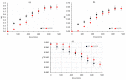
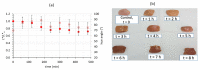
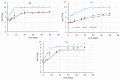
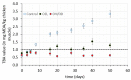
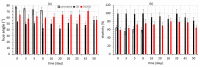
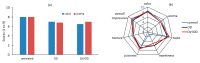
The scope of this work is the study of a combined process including a dipping step into an oregano (Origanum vulgare ssp. hirtum) infusion (OV) followed by osmotic treatment of chicken fillets at 15 °C. Chicken fillets were immersed in an osmotic solution consisting of 40% glycerol and 5% NaCl with (OV/OD) and without (OD) prior antioxidant enrichment in a hypotonic oregano solution. A comparative shelf life study of all the samples (untreated, OD and OV/OD treated) was then conducted at 4 °C in order to assess the impact of this process on the quality and shelf life of chilled chicken fillets. Microbial growth, lipid oxidation and color/texture changes were measured throughout the chilled storage period. Rates of microbial growth of pretreated fillets were significantly reduced, mainly as a result of water activity decrease (OD step). Rancidity development closely related to off odors and sensory rejection was greatly inhibited in treated fillets owing to both inhibitory factors (OD and OV), with water-soluble phenols (OV step) exhibiting the main antioxidant effect. Shelf life of treated chicken fillets exhibited a more than three-fold increase as compared to the untreated samples based on both chemical and microbial spoilage indices, maintaining a positive and pleasant sensory profile throughout the storage period examined.
Keywords: Origanum vulgare; chicken fillets; hurdle technology; osmotic treatment; shelf life improvement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chitosan boosts the antimicrobial activity of Origanum vulgare essential oil in modified atmosphere packaged pork.Food Microbiol. 2016 Oct;59:23-31. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2016.05.007. Epub 2016 May 11. Food Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27375241
-
Chitosan dipping or oregano oil treatments, singly or combined on modified atmosphere packaged chicken breast meat.Int J Food Microbiol. 2012 Jun 1;156(3):264-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2012.04.002. Epub 2012 Apr 6. Int J Food Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22534355
-
Combined effect of oregano essential oil and modified atmosphere packaging on shelf-life extension of fresh chicken breast meat, stored at 4 degrees C.Food Microbiol. 2007 Sep;24(6):607-17. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2006.12.005. Epub 2007 Jan 12. Food Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17418312
-
Meta-analysis of citrus-derived additives on chicken meat quality and safety: a comprehensive evaluation of acceptability, physicochemical properties, and microbial contamination.Poult Sci. 2024 May;103(5):103556. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.103556. Epub 2024 Feb 15. Poult Sci. 2024. PMID: 38430777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Northern shrimp (Pandalus borealis) - a review on biology, catch, processing, quality changes, shelf-life and product safety.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2025 May 24:1-34. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2025.2505241. Online ahead of print. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40411766 Review.
References
-
- Biswas A.K., Chatli M.K., Jairath G. Natural antioxidants in poultry products. In: Banerjee R., Verma A.K., Siddiqui M.W., editors. Natural Antioxidants: Applications in Foods of Animal Origin. Apple Academic Press, Inc.; Point Pleasant, NJ, USA: 2017. pp. 165–202.
-
- Majdinasab M., Niakousari M., Shaghaghian S., Dehghani H. Antimicrobial and antioxidant coating based on basil seed gum incorporated with Shirazi thyme and summer savory essential oils emulsions for shelf-life extension of refrigerated chicken fillets. Food Hydrocoll. 2020;108:106011. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.106011. - DOI
-
- Latou E., Mexis S., Badeka A., Kontakos S., Kontominas M. Combined effect of chitosan and modified atmosphere packaging for shelf life extension of chicken breast fillets. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2014;55:263–268. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2013.09.010. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

