Estimation of Undetected Asymptomatic COVID-19 Cases in South Korea Using a Probabilistic Model
- PMID: 34066512
- PMCID: PMC8124955
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18094946
Estimation of Undetected Asymptomatic COVID-19 Cases in South Korea Using a Probabilistic Model
Abstract
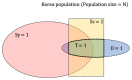
Increasing evidence shows that many infections of COVID-19 are asymptomatic, becoming a global challenge, since asymptomatic infections have the same infectivity as symptomatic infections. We developed a probabilistic model for estimating the proportion of undetected asymptomatic COVID-19 patients in the country. We considered two scenarios: one is conservative and the other is nonconservative. By combining the above two scenarios, we gave an interval estimation of 0.0001-0.0027 and in terms of the population, 5200-139,900 is the number of undetected asymptomatic cases in South Korea as of 2 February 2021. In addition, we provide estimates for total cases of COVID-19 in South Korea. Combination of undetected asymptomatic cases and undetected symptomatic cases to the number of confirmed cases (78,844 cases on 2 February 2021) shows that 0.17-0.42% (89,244-218,744) of the population have COVID-19. In conclusion, to control and understand the true ongoing reality of the pandemic, it is of outermost importance to focus on the ratio of undetected asymptomatic cases in the total population.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; asymptomatic; probabilistic model; screening; undetected.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The proportion of COVID-19 cases that are asymptomatic in South Korea: Comment on Nishiura et al.Int J Infect Dis. 2020 Jul;96:398. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.05.037. Epub 2020 May 14. Int J Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32417245 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Characteristics of Asymptomatic Patients with COVID-19: A Nationwide Cohort Study in South Korea.Int J Infect Dis. 2020 Oct;99:266-268. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.08.001. Epub 2020 Aug 6. Int J Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32771632 Free PMC article.
-
The high prevalence of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection reveals the silent spread of COVID-19.Int J Infect Dis. 2021 Apr;105:656-661. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2021.02.100. Epub 2021 Feb 26. Int J Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33647516 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 viral shedding and susceptibility: perspectives on gender and asymptomatic patients.J Infect Dev Ctries. 2022 May 30;16(5):768-777. doi: 10.3855/jidc.14721. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2022. PMID: 35656946 Review.
-
Ratio of asymptomatic COVID-19 cases among ascertained SARS-CoV-2 infections in different regions and population groups in 2020: a systematic review and meta-analysis including 130 123 infections from 241 studies.BMJ Open. 2021 Dec 7;11(12):e049752. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-049752. BMJ Open. 2021. PMID: 34876424 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Role of Asymptomatic COVID-19 Cases in Viral Transmission: Findings From a Hierarchical Community Contact Network Model.IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng. 2021 Sep 3;19(2):576-585. doi: 10.1109/TASE.2021.3106782. eCollection 2022 Apr. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng. 2021. PMID: 35582345 Free PMC article.
-
Modified susceptible-exposed-infectious-recovered model for assessing the effectiveness of non-pharmaceutical interventions during the COVID-19 pandemic in Seoul.J Theor Biol. 2023 Jan 21;557:111329. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2022.111329. Epub 2022 Oct 26. J Theor Biol. 2023. PMID: 36309117 Free PMC article.
-
New framework to assess tracing and testing based on South Korea's response to COVID-19.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 May 3;24(1):469. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09363-4. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38702610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mathematical Modeling of COVID-19 Transmission and Intervention in South Korea: A Review of Literature.Yonsei Med J. 2023 Jan;64(1):1-10. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2022.0471. Yonsei Med J. 2023. PMID: 36579373 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early and long term antibody kinetics of asymptomatic and mild disease COVID-19 patients.Sci Rep. 2021 Jul 2;11(1):13780. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-93175-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34215811 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Richardson S., Hirsch J.S., Narasimhan M., Crawford J.M., McGinn T., Davidson K.W., Barnaby D.P., Becker L.B., Chelico J.D., Cohen S.L., et al. Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City area. JAMA. 2020;323:2052–2059. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.6775. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Susilo A., Rumende C.M., Pitoyo C.W., Santoso W.D., Yulianti M., Herikurniawan H., Sinto R., Singh G., Nainggolan L., Nelwan E.J., et al. Coronavirus disease 2019: Tinjauan literatur terkini. J. Penyakit Dalam Indones. 2020;7:45–67. doi: 10.7454/jpdi.v7i1.415. - DOI
-
- WHO . Laboratory Testing for 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in Suspected Human Cases: Interim Guidance, 14 January 2020. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

