Cannabinoids, Phenolics, Terpenes and Alkaloids of Cannabis
- PMID: 34066753
- PMCID: PMC8125862
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26092774
Cannabinoids, Phenolics, Terpenes and Alkaloids of Cannabis
Abstract
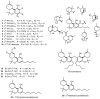
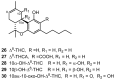
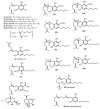
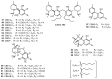
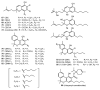
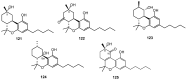
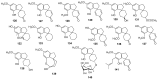
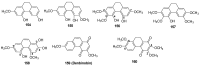
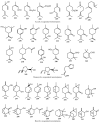
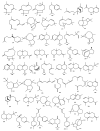
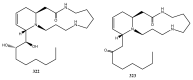
Cannabis sativa is one of the oldest medicinal plants in the world. It was introduced into western medicine during the early 19th century. It contains a complex mixture of secondary metabolites, including cannabinoids and non-cannabinoid-type constituents. More than 500 compounds have been reported from C. sativa, of which 125 cannabinoids have been isolated and/or identified as cannabinoids. Cannabinoids are C21 terpeno-phenolic compounds specific to Cannabis. The non-cannabinoid constituents include: non-cannabinoid phenols, flavonoids, terpenes, alkaloids and others. This review discusses the chemistry of the cannabinoids and major non-cannabinoid constituents (terpenes, non-cannabinoid phenolics, and alkaloids) with special emphasis on their chemical structures, methods of isolation, and identification.
Keywords: Cannabis sativa; alkaloids; cannabinoids; flavonoids; non-cannabinoid phenols; terpenes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

