A Comparison of the Level of Acceptance and Hesitancy towards the Influenza Vaccine and the Forthcoming COVID-19 Vaccine in the Medical Community
- PMID: 34066790
- PMCID: PMC8150871
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines9050475
A Comparison of the Level of Acceptance and Hesitancy towards the Influenza Vaccine and the Forthcoming COVID-19 Vaccine in the Medical Community
Abstract
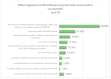
Despite research conducted worldwide, there is no treatment specifically targeting SARS-CoV-2 infection with efficacy proven by randomized controlled trials. A chance for a breakthrough is vaccinating most of the global population. Public opinion surveys on vaccine hesitancy prompted our team to investigate Polish healthcare workers' (HCWs) attitudes towards the SARS-CoV-2 and influenza vaccinations. In-person and online surveys of HCWs: doctors, nurses, medical students, and other allied health professionals (n = 419) were conducted between 14 September 2020 and 5 November 2020. In our study, 68.7% of respondents would like to be vaccinated against COVID-19. The safety and efficacy of COVID-19 vaccinations would persuade 86.3% of hesitant and those who would refuse to be vaccinated. 3.1% of all respondents claimed that no argument would convince them to get vaccinated. 61.6% of respondents declared a willingness to receive an influenza vaccination, of which 83.3% were also inclined to receive COVID-19 vaccinations. Although most respondents-62.5% (262/419) indicated they trusted in the influenza vaccine more, more respondents intended to get vaccinated against COVID-19 in the 2020/2021 season. The study is limited by its nonrandom sample of HCWs but provides a preliminary description of attitudes towards SARS-CoV-2 vaccination.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; flu vaccine; healthcare workers; influenza; vaccine; vaccine hesitancy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Docherty A.B., Harrison E.M., Green C.A., Hardwick H.E., Pius R., Norman L., Holden K.A., Read J.M., Dondelinger F., Carson G., et al. Features of 20,133 UK patients in hospital with covid-19 using the ISARIC WHO Clinical Characterisation Protocol: Prospective observational cohort study. BMJ. 2020;369:m1985. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m1985. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous