Protective Effects of Swertiamarin against Methylglyoxal-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition by Improving Oxidative Stress in Rat Kidney Epithelial (NRK-52E) Cells
- PMID: 34067107
- PMCID: PMC8125635
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26092748
Protective Effects of Swertiamarin against Methylglyoxal-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition by Improving Oxidative Stress in Rat Kidney Epithelial (NRK-52E) Cells
Abstract
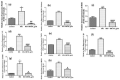
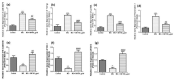
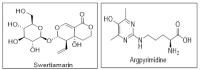
Increased blood glucose in diabetic individuals results in the formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs), causing various adverse effects on kidney cells, thereby leading to diabetic nephropathy (DN). In this study, the antiglycative potential of Swertiamarin (SM) isolated from the methanolic extract of E. littorale was explored. The effect of SM on protein glycation was studied by incubating bovine serum albumin with fructose at 60 °C in the presence and absence of different concentrations of swertiamarin for 24 h. For comparative analysis, metformin was also used at similar concentrations as SM. Further, to understand the role of SM in preventing DN, in vitro studies using NRK-52E cells were done by treating cells with methylglyoxal (MG) in the presence and absence of SM. SM showed better antiglycative potential as compared to metformin. In addition, SM could prevent the MG mediated pathogenesis in DN by reducing levels of argpyrimidine, oxidative stress and epithelial mesenchymal transition in kidney cells. SM also downregulated the expression of interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-1β. This study, for the first time, reports the antiglycative potential of SM and also provides novel insights into the molecular mechanisms by which SM prevents toxicity of MG on rat kidney cells.
Keywords: AGE-inhibitor; advanced glycation end product (AGE); diabetic nephropathy; epithelial to mesenchymal transition; oxidative stress; swertiamarin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Swertiamarin mitigates nephropathy in high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats by inhibiting the formation of advanced glycation end products.Arch Physiol Biochem. 2024 Apr;130(2):136-154. doi: 10.1080/13813455.2021.1987478. Epub 2021 Oct 16. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2024. PMID: 34657540
-
Protective role of Clitoria ternatea L. flower extract on methylglyoxal-induced protein glycation and oxidative damage to DNA.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021 Mar 1;21(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s12906-021-03255-9. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021. PMID: 33648500 Free PMC article.
-
Bimolecular interaction of argpyrimidine (a Maillard reaction product) in in vitro non-enzymatic protein glycation model and its potential role as an antiglycating agent.Int J Biol Macromol. 2017 Sep;102:1274-1285. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.04.108. Epub 2017 May 6. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017. PMID: 28487198
-
Chemistry, Pharmacology and Therapeutic Potential of Swertiamarin - A Promising Natural Lead for New Drug Discovery and Development.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021 Jun 21;15:2721-2746. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S299753. eCollection 2021. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021. PMID: 34188450 Free PMC article.
-
The Molecular Targets of Swertiamarin and its Derivatives Confer Anti- Diabetic and Anti-Hyperlipidemic Effects.Curr Drug Targets. 2018;19(16):1958-1967. doi: 10.2174/1389450119666180406113428. Curr Drug Targets. 2018. PMID: 29623834 Review.
Cited by
-
The Therapeutic Effect and Mechanism of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2025 May 15;18:1599-1627. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S517874. eCollection 2025. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2025. PMID: 40391051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress in Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacological Effects, and Molecular Mechanisms of Swertiamarin: A Comprehensive Review.Cells. 2025 Jul 30;14(15):1173. doi: 10.3390/cells14151173. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40801607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phenolic Compounds from Mori Cortex Ameliorate Sodium Oleate-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Fibrosis in NRK-52e Cells through CD36.Molecules. 2021 Oct 11;26(20):6133. doi: 10.3390/molecules26206133. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34684716 Free PMC article.
-
Cardioprotective Role of Swertiamarin, a Plant Glycoside Against Experimentally Induced Myocardial Infarction via Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Functions.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2023 Sep;195(9):5394-5408. doi: 10.1007/s12010-022-04094-1. Epub 2022 Aug 12. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 35960488
-
Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized from Enicostemma littorale Exhibit Gut Tight Junction Restoration and Hepatoprotective Activity via Regulation of the Inflammatory Pathway.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Jul 9;17(7):895. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17070895. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40733103 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Writing Team for the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications Research Group Sustained Effect of Intensive Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus on Development and Progression of Diabetic Nephropathy. JAMA. 2003;290:2159–2167. doi: 10.1001/jama.290.16.2159. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barbosa J., Steffes M.W., E Sutherland D., E Connett J., Rao K.V., Mauer S.M. Effect of glycemic control on early diabetic renal lesions. A 5-year randomized controlled clinical trial of insulin-dependent diabetic kidney transplant recipients. JAMA. 1994;272:600–606. doi: 10.1001/jama.1994.03520080042041. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

