Water-Food Nexus Assessment in Agriculture: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 34067130
- PMCID: PMC8124841
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18094983
Water-Food Nexus Assessment in Agriculture: A Systematic Review
Abstract
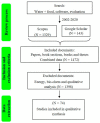
The Water-Food Nexus (WF) has been proposed to reach equitable, balanced, and sustainable access to water and food resources in the face of the growing population demand. Therefore, developing models to assess them has become more relevant. This work systematically reviews the literature on the tools used to evaluate water and food resources between 2002 and 2020. Furthermore, it reports a critical analysis of the software used to assess the WF Nexus quantitatively. The models analyzed were Life Cycle Assessment (LCA), Common Agricultural Policy Regional Impact (CAPRI), Global Food and Water System (GFWS), Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT), Water Evaluation And Planning system (WEAP), and Soil Water Atmosphere Plant (SWAP). We deduced that the following are necessary in evaluating the WF Nexus: (1) the capacity to generate future scenarios, (2) a global application, and (3) the application in case studies. The present paper is the first review to provide an overview of the software applied to evaluate WF Nexus, including the advantages and disadvantages of the tools found. They can help build sustainability criteria when designing policies that reduce water and food security risks and promote efficient water and food use.
Keywords: CAPRI; GFWS; LCA; SWAT; WEAP; WF Nexus; crops.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Elements of the water - food - environment nexus for integrated sustainability analysis.Sci Total Environ. 2023 Dec 20;905:166866. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.166866. Epub 2023 Sep 9. Sci Total Environ. 2023. PMID: 37678519
-
Energy simulation modeling for water-energy-food nexus system: a systematic review.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023 Jan;30(3):5487-5501. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-24300-1. Epub 2022 Nov 24. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023. PMID: 36418836
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Comparison of cellulose, modified cellulose and synthetic membranes in the haemodialysis of patients with end-stage renal disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(3):CD003234. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003234. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;(3):CD003234. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003234.pub2. PMID: 11687058 Updated.
Cited by
-
The Impact of Sustainability Goals on Productivity Growth: The Moderating Role of Global Warming.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Oct 20;18(21):11034. doi: 10.3390/ijerph182111034. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34769553 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maja M.M., Ayano S.F. The Impact of Population Growth on Natural Resources and Farmers’ Capacity to Adapt to Climate Change in Low-Income Countries. Earth Syst. Environ. 2021 doi: 10.1007/s41748-021-00209-6. - DOI
-
- Rasul G. Managing the food, water, and energy nexus for achieving the Sustainable Development Goals in South Asia. Environ. Dev. 2016;18:14–25. doi: 10.1016/j.envdev.2015.12.001. - DOI
-
- Ferroukhi R., Nagpal D., López P.Á., Hodges T., Mohtar R., Daher B., Mohtar S., Keulertz M. Renewable Energy in the Water, Energy & Food Nexus. International Renewable Energy Agency; Masdar City, Abu Dhabi: 2015. pp. 24–35.
-
- Mannan M., Al-Ansari T., Mackey H.R., Al-Ghamdi S.G. Quantifying the energy, water and food nexus: A review of the latest developments based on life-cycle assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2018;193:300–314. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.05.050. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

