Extracellular Vesicles and Asthma-More Than Just a Co-Existence
- PMID: 34067156
- PMCID: PMC8124625
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22094984
Extracellular Vesicles and Asthma-More Than Just a Co-Existence
Abstract
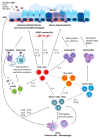
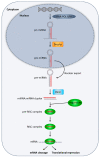
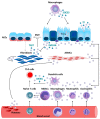
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are membranous structures, which are secreted by almost every cell type analyzed so far. In addition to their importance for cell-cell communication under physiological conditions, EVs are also released during pathogenesis and mechanistically contribute to this process. Here we summarize their functional relevance in asthma, one of the most common chronic non-communicable diseases. Asthma is a complex persistent inflammatory disorder of the airways characterized by reversible airflow obstruction and, from a long-term perspective, airway remodeling. Overall, mechanistic studies summarized here indicate the importance of different subtypes of EVs and their variable cargoes in the functioning of the pathways underlying asthma, and show some interesting potential for the development of future therapeutic interventions. Association studies in turn demonstrate a good diagnostic potential of EVs in asthma.
Keywords: airway; allergy; asthma; epigenetic(-s); exosome; extracellular vesicle (EV); inflammation; microRNA (miRNA); microvesicle (MV).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors report no potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- WHO The Top 10 Causes of Death. [(accessed on 18 April 2021)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death.
-
- WHO WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard: With Vaccination Data. [(accessed on 18 April 2021)]; Available online: https://covid19.who.int/
-
- Camps J., García-Heredia A. Introduction: Oxidation and inflammation, a molecular link between non-communicable diseases. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014;824:1–4. - PubMed
-
- Pahwa R., Goyal A., Bansal P., Jialal I. Chronic Inflammation. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2021. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

