Diagnostic Challenges in Epithelioid Pleural Mesothelioma: Case Series with Support from Electron Microscopy
- PMID: 34067170
- PMCID: PMC8150908
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics11050841
Diagnostic Challenges in Epithelioid Pleural Mesothelioma: Case Series with Support from Electron Microscopy
Abstract
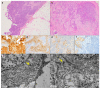
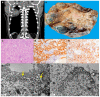
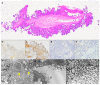
The histological diagnosis of pleural epithelioid mesothelioma can be difficult in the case of rare variants or in the definition of neoplasm origin in patients with previous or concomitant tumours. Currently, several immunohistochemical reactions are available in the surgical pathologist's armamentarium that allow us to obtain a more sensitive and specific diagnosis of malignant pleural mesothelioma. However, in some cases, the final interpretation remains inconclusive. Historically, ultrastructural examination has represented a useful tool for the definition of the mesothelial nature of neoplastic cells due to their peculiar morphological characteristics. The recent international guidelines for pathological diagnosis of pleural mesothelioma suggest the use of electron microscopy when the immunohistochemical reactions are equivocal or when further support of a diagnosis of mesothelioma is needed. This paper presents three cases of pleural epithelioid mesothelioma whose diagnoses were finally supported by ultrastructural examination.
Keywords: histology; immunohistochemistry; mesothelioma; transmission electron microscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The use of histological and immunohistochemical markers to distinguish pleural malignant mesothelioma and in situ mesothelioma from reactive mesothelial hyperplasia and reactive pleural fibrosis.J Pathol. 1999 Oct;189(2):251-7. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(199910)189:2<251::AID-PATH412>3.0.CO;2-F. J Pathol. 1999. PMID: 10547583
-
Primary thymic epithelial tumours of the pleura mimicking malignant mesothelioma.Histopathology. 2002 Jul;41(1):42-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2559.2002.01422.x. Histopathology. 2002. PMID: 12121236
-
Diagnostic efficacy of electron microscopy and pleural effusion cytology for the distinction of pleural mesothelioma and lung adenocarcinoma.Ultrastruct Pathol. 2016 Sep-Oct;40(5):254-60. doi: 10.1080/01913123.2016.1195469. Epub 2016 Jul 12. Ultrastruct Pathol. 2016. PMID: 27405014
-
Primary pleural epithelioid mesothelioma of clear cell type: a case report and review of current literature.Ultrastruct Pathol. 2011 Dec;35(6):267-70. doi: 10.3109/01913123.2011.606965. Epub 2011 Oct 6. Ultrastruct Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21978187 Review.
-
Pathohistological diagnosis and differential diagnosis.Recent Results Cancer Res. 2011;189:57-78. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-10862-4_5. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21479896 Review.
Cited by
-
Deciduosis in a cesarean scar.Autops Case Rep. 2022 May 6;12:e2021383. doi: 10.4322/acr.2021.383. eCollection 2022. Autops Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35574043 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptophysin, CD117, and GATA3 as a Diagnostic Immunohistochemical Panel for Small Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Urinary Tract.Cancers (Basel). 2022 May 19;14(10):2495. doi: 10.3390/cancers14102495. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35626098 Free PMC article.
-
Intrapulmonary Biphasic Mesothelioma Misdiagnosed as Adenocarcinoma: Case Report and a Potential Diagnostic Pitfall.Onco Targets Ther. 2024 Nov 5;17:925-931. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S477916. eCollection 2024. Onco Targets Ther. 2024. PMID: 39525355 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carbone M., Adusumilli P.S., Alexander H.R., Jr., Baas P., Bardelli F., Bononi A., Bueno R., Felley-Bosco E., Galateau-Salle F., Jablons D., et al. Mesothelioma: Scientific clues for prevention, diagnosis, and therapy. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019;69:402–429. doi: 10.3322/caac.21572. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Galateau-Salle F., Churg A., Roggli V., Travis W.D., World Health Organization Committee for Tumors of the Pleura The 2015 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Pleura: Advances since the 2004 Classification. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016;11:142–154. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2015.11.005. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Husain A.N., Colby T.V., Ordóñez N.G., Allen T.C., Attanoos R.L., Beasley M.B., Butnor K.J., Chirieac L.R., Churg A.M., Dacic S., et al. Guidelines for Pathologic Diagnosis of Malignant Mesothelioma 2017 Update of the Consensus Statement from the International Mesothelioma Interest Group. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2018;142:89–108. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2017-0124-RA. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

