A Systematic Review of Oropharyngeal Dysphagia Models in Rodents
- PMID: 34067192
- PMCID: PMC8125817
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18094987
A Systematic Review of Oropharyngeal Dysphagia Models in Rodents
Abstract
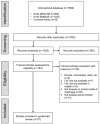
Oropharyngeal dysphagia is a condition characterized by swallowing difficulty in the mouth and pharynx, which can be due to various factors. Animal models of oropharyngeal dysphagia are essential to confirm the cause-specific symptoms, pathological findings, and the effect of treatment. Recently, various animal models of dysphagia have been reported. The purpose of this review is to organize the rodent models of oropharyngeal dysphagia reported to date. The articles were obtained from Medline, Embase, and the Cochrane library, and selected following the PRISMA guideline. The animal models in which oropharyngeal dysphagia was induced in rats or mice were selected and classified based on the diseases causing oropharyngeal dysphagia. The animal used, method of inducing dysphagia, and screening methods and results were collected from the selected 37 articles. Various rodent models of oropharyngeal dysphagia provide distinctive information on atypical swallowing. Applying and analyzing the treatment in rodent models of dysphagia induced from various causes is an essential process to develop symptom-specific treatments. Therefore, the results of this study provide fundamental and important data for selecting appropriate animal models to study dysphagia.
Keywords: mice; oropharyngeal dysphagia; rats; swallowing difficulty.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Review of the effectiveness of neuromuscular electrical stimulation in the treatment of dysphagia - an update.Ger Med Sci. 2022 Jun 14;20:Doc08. doi: 10.3205/000310. eCollection 2022. Ger Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35875244 Free PMC article.
-
Psychopathological aspects of dysphagia: a systematic review on correlations with eating disorders and other psychiatric conditions.Eat Weight Disord. 2022 Apr;27(3):881-892. doi: 10.1007/s40519-021-01227-z. Epub 2021 Jul 2. Eat Weight Disord. 2022. PMID: 34213745
-
Modifying the consistency of food and fluids for swallowing difficulties in dementia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Sep 24;9(9):CD011077. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011077.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30251253 Free PMC article.
-
Screening for aspiration risk associated with dysphagia in acute stroke.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Oct 18;10(10):CD012679. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012679.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34661279 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of voice training interventions on patients with oropharyngeal dysphagia: a systematic review.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2023 Mar;280(3):973-984. doi: 10.1007/s00405-022-07719-7. Epub 2022 Nov 7. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2023. PMID: 36342516 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Bioenergetic Evaluation of Muscle Fatigue in Murine Tongue.Dysphagia. 2023 Aug;38(4):1039-1048. doi: 10.1007/s00455-022-10537-y. Epub 2022 Nov 19. Dysphagia. 2023. PMID: 36401630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Swallowing-related muscle inflammation and fibrosis induced by a single dose of radiation exposure in mice.Lab Anim Res. 2024 Apr 1;40(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s42826-024-00199-2. Lab Anim Res. 2024. PMID: 38561867 Free PMC article.
-
Altered tongue muscle contractile properties coincide with altered swallow function in the adult Ts65Dn mouse model of down syndrome.Front Neurol. 2024 Mar 22;15:1384572. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1384572. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38585362 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gallegos C., de la Fuente E.B., Clave P., Costa A., Assegehegn G. Nutritional aspects of dysphagia management. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2017;81:271–318. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical