Urine and Plasma Metabolome of Healthy Adults Consuming the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) Diet: A Randomized Pilot Feeding Study
- PMID: 34067295
- PMCID: PMC8224662
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13061768
Urine and Plasma Metabolome of Healthy Adults Consuming the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) Diet: A Randomized Pilot Feeding Study
Abstract
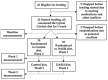
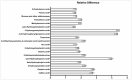
We aimed to identify plasma and urine metabolites altered by the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet in a post-hoc analysis of a pilot feeding trial. Twenty adult participants with un-medicated hypertension consumed a Control diet for one week followed by 2 weeks of random assignment to either Control or DASH diet. Non-missing fasting plasma (n = 56) and 24-h urine (n = 40) were used to profile metabolites using untargeted gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Linear models were used to compare metabolite levels between the groups. In urine, 19 identifiable untargeted metabolites differed between groups at p < 0.05. These included a variety of phenolic acids and their microbial metabolites that were higher during the DASH diet, with many at false discovery rate (FDR) adjusted p < 0.2. In plasma, eight identifiable untargeted metabolites were different at p < 0.05, but only gamma-tocopherol was significantly lower on DASH at FDR adjusted p < 0.2. The results provide insights into the mechanisms of benefit of the DASH diet.
Keywords: DASH; blood pressure; metabolomics; nutrition; polyphenols.
Conflict of interest statement
J.J.S. has received consulting fees from Tricida. The authors declare no other conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Vollmer W.M., Sacks F.M., Ard J., Appel L.J., Bray G.A., Simons-Morton D.G., Conlin P.R., Svetkey L.P., Erlinger T.P., Moore T.J. Effects of diet and sodium intake on blood pressure: Subgroup analysis of the DASH-sodium trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2001;135:1019–1028. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-135-12-200112180-00005. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Salehi-Abargouei A., Maghsoudi Z., Shirani F., Azadbakht L. Effects of Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH)-style diet on fatal or nonfatal cardiovascular diseases–incidence: A systematic review and meta-analysis on observational prospective studies. Nutrition. 2013;29:611–618. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2012.12.018. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

