Recent Findings on Thymoquinone and Its Applications as a Nanocarrier for the Treatment of Cancer and Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 34067322
- PMCID: PMC8224699
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13060775
Recent Findings on Thymoquinone and Its Applications as a Nanocarrier for the Treatment of Cancer and Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
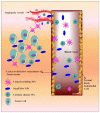
Cancer causes a considerable amount of mortality in the world, while arthritis is an immunological dysregulation with multifactorial pathogenesis including genetic and environmental defects. Both conditions have inflammation as a part of their pathogenesis. Resistance to anticancer and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) happens frequently through the generation of energy-dependent transporters, which lead to the expulsion of cellular drug contents. Thymoquinone (TQ) is a bioactive molecule with anticancer as well as anti-inflammatory activities via the downregulation of several chemokines and cytokines. Nevertheless, the pharmacological importance and therapeutic feasibility of thymoquinone are underutilized due to intrinsic pharmacokinetics, including short half-life, inadequate biological stability, poor aqueous solubility, and low bioavailability. Owing to these pharmacokinetic limitations of TQ, nanoformulations have gained remarkable attention in recent years. Therefore, this compilation intends to critically analyze recent advancements in rheumatoid arthritis and cancer delivery of TQ. This literature search revealed that nanocarriers exhibit potential results in achieving targetability, maximizing drug internalization, as well as enhancing the anti-inflammatory and anticancer efficacy of TQ. Additionally, TQ-NPs (thymoquinone nanoparticles) as a therapeutic payload modulated autophagy as well as enhanced the potential of other drugs when given in combination. Moreover, nanoformulations improved pharmacokinetics, drug deposition, using EPR (enhanced permeability and retention) and receptor-mediated delivery, and enhanced anti-inflammatory and anticancer properties. TQ's potential to reduce metal toxicity, its clinical trials and patents have also been discussed.
Keywords: arthritis; cancer; nanotechnology; synovial delivery; thymoquinone; toxicity reduction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Influence of Pluronic F68 and F127 Nanocarrier on Physicochemical Properties, In vitro Release, and Antiproliferative Activity of Thymoquinone Drug.Pharmacognosy Res. 2017 Jan-Mar;9(1):12-20. doi: 10.4103/0974-8490.199774. Pharmacognosy Res. 2017. PMID: 28250648 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of pro-inflammatory markers IL-6 and TNF-α in rheumatoid arthritis using nano-lipidic carriers of a quinone-based phenolic: an in vitro and in vivo study.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2023 Feb;13(2):627-641. doi: 10.1007/s13346-022-01221-7. Epub 2022 Aug 14. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 35963927
-
Enhancing the Anti-Leukemic Potential of Thymoquinone/Sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin (SBE-β-CD) Inclusion Complexes.Biomedicines. 2023 Jul 4;11(7):1891. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11071891. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37509531 Free PMC article.
-
Thymoquinone a Potential Therapeutic Molecule from the Plant Nigella sativa: Role of Colloidal Carriers in its Effective Delivery.Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2018;12(1):3-22. doi: 10.2174/1872211311666171129121128. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2018. PMID: 29189187 Review.
-
Thymoquinone (2-Isoprpyl-5-methyl-1, 4-benzoquinone) as a chemopreventive/anticancer agent: Chemistry and biological effects.Saudi Pharm J. 2019 Dec;27(8):1113-1126. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2019.09.008. Epub 2019 Sep 25. Saudi Pharm J. 2019. PMID: 31885471 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of the PTEN Tumor Suppressor Gene and Its Anti-Angiogenic Activity in Melanoma and Other Cancers.Molecules. 2024 Feb 4;29(3):721. doi: 10.3390/molecules29030721. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38338464 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antinociceptive Action of Thymoquinone-Loaded Liposomes in an In Vivo Model of Tendinopathy.Pharmaceutics. 2023 May 17;15(5):1516. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15051516. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37242757 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological modes of plant-derived compounds for targeting inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis: A comprehensive review on immunomodulatory perspective.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Apr;33(4):1537-1581. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01664-7. Epub 2025 Mar 13. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40074996 Review.
-
Thymoquinone: Review of Its Potential in the Treatment of Neurological Diseases.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Mar 27;15(4):408. doi: 10.3390/ph15040408. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35455405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Integrated bioinformatics analysis for differential gene expression with identification of hub genes and lncRNA.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2022 Apr 16;30:101262. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2022.101262. eCollection 2022 Jul. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2022. PMID: 35479061 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rathore C., Upadhyay N.K., Sharma A., Lal U.R., Raza K., Negi P. Phospholipid nanoformulation of thymoquinone with enhanced bioavailability: Development, characterization and anti-inflammatory activity. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019;52:316–324. doi: 10.1016/j.jddst.2019.04.041. - DOI
-
- Wang X., Fang G., Yang Y., Pang Y. The newly discovered natural compounds against rheumatoid arthritis—An overview. Phytochem. Lett. 2019;34:50–58. doi: 10.1016/j.phytol.2019.09.011. - DOI
-
- Ansari M.O., Parveen N., Ahmad F., Wani A.L., Afrin S., Rahman Y., Jameel S., Khan Y.A., Siddique H.R., Tabish M., et al. Evaluation of DNA interaction, genotoxicity and oxidative stress induced by iron oxide nanoparticles both in vitro and in vivo: Attenuation by thymoquinone. Sci. Rep. 2019;9:1–14. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-43188-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

