Fatty Acid Desaturases: Uncovering Their Involvement in Grapevine Defence against Downy Mildew
- PMID: 34067363
- PMCID: PMC8196838
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22115473
Fatty Acid Desaturases: Uncovering Their Involvement in Grapevine Defence against Downy Mildew
Abstract
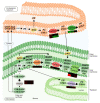
Grapevine downy mildew, caused by the biotrophic oomycete Plasmopara viticola, is one of the most severe and devastating diseases in viticulture. Unravelling the grapevine defence mechanisms is crucial to develop sustainable disease control measures. Here we provide new insights concerning fatty acid's (FA) desaturation, a fundamental process in lipid remodelling and signalling. Previously, we have provided evidence that lipid signalling is essential in the establishment of the incompatible interaction between grapevine and Plasmopara viticola. In the first hours after pathogen challenge, jasmonic acid (JA) accumulation, activation of its biosynthetic pathway and an accumulation of its precursor, the polyunsaturated α-linolenic acid (C18:3), were observed in the leaves of the tolerant genotype, Regent. This work was aimed at a better comprehension of the desaturation processes occurring after inoculation. We characterised, for the first time in Vitis vinifera, the gene family of the FA desaturases and evaluated their involvement in Regent response to Plasmopara viticola. Upon pathogen challenge, an up-regulation of the expression of plastidial FA desaturases genes was observed, resulting in a higher content of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) of chloroplast lipids. This study highlights FA desaturases as key players in membrane remodelling and signalling in grapevine defence towards biotrophic pathogens.
Keywords: Plasmopara viticola; Vitis vinifera; biotrophy; fatty acid desaturases; fatty acid modulation; lipid signalling; plant defence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
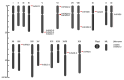
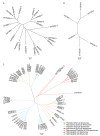


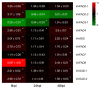
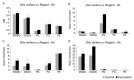
References
-
- Gessler C., Pertot I., Perazzolli M. Plasmopara viticola: A review of knowledge on downy mildew of grapevine and effective disease management. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2011;50:3–44. doi: 10.14601/Phytopathol_Mediterr-9360. - DOI
-
- Singh S.C., Sinha R.P., Häder D.-P. Role of Lipids and Fatty Acids in Stress Tolerance in Cyanobacteria. Acta Protozool. 2002;41:297–308.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

