Generators of Pressure-Evoked Currents in Vertebrate Outer Retinal Neurons
- PMID: 34067375
- PMCID: PMC8224636
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10061288
Generators of Pressure-Evoked Currents in Vertebrate Outer Retinal Neurons
Abstract
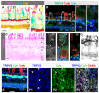
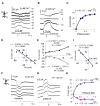
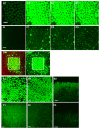
(1) Background: High-tension glaucoma damages the peripheral vision dominated by rods. How mechanosensitive channels (MSCs) in the outer retina mediate pressure responses is unclear. (2) Methods: Immunocytochemistry, patch clamp, and channel fluorescence were used to study MSCs in salamander photoreceptors. (3) Results: Immunoreactivity of transient receptor potential channel vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) was revealed in the outer plexiform layer, K+ channel TRAAK in the photoreceptor outer segment (OS), and TRPV2 in some rod OS disks. Pressure on the rod inner segment evoked sustained currents of three components: (A) the inward current at <-50 mV (Ipi), sensitive to Co2+; (B) leak outward current at ≥-80 mV (Ipo), sensitive to intracellular Cs+ and ruthenium red; and (C) cation current reversed at ~10 mV (Ipc). Hypotonicity induced slow currents like Ipc. Environmental pressure and light increased the FM 1-43-identified open MSCs in the OS membrane, while pressure on the OS with internal Cs+ closed a Ca2+-dependent current reversed at ~0 mV. Rod photocurrents were thermosensitive and affected by MSC blockers. (4) Conclusions: Rods possess depolarizing (TRPV) and hyperpolarizing (K+) MSCs, which mediate mutually compensating currents between -50 mV and 10 mV, serve as an electrical cushion to minimize the impact of ocular mechanical stress.
Keywords: TRPV; confocal microscopy; immunofluorescence; mechanosensitive channel; patch clamping; potassium channel; rod; temperature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

