Endocannabinoid System and Its Regulation by Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Full Spectrum Hemp Oils
- PMID: 34067450
- PMCID: PMC8196941
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22115479
Endocannabinoid System and Its Regulation by Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Full Spectrum Hemp Oils
Abstract
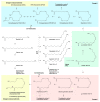
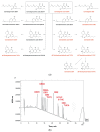
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) consists of endogenous cannabinoids, their receptors, and metabolic enzymes that play a critical homeostatic role in modulating polyunsaturated omega fatty acid (PUFA) signaling to maintain a balanced inflammatory and redox state. Whole food-based diets and dietary interventions linked to PUFAs of animal (fish, calamari, krill) or plant (hemp, flax, walnut, algae) origin, as well as full-spectrum hemp oils, are increasingly used to support the ECS tone, promote healthy metabolism, improve risk factors associated with cardiovascular disorders, encourage brain health and emotional well-being, and ameliorate inflammation. While hemp cannabinoids of THC and CBD groups show distinct but complementary actions through a variety of cannabinoid (CB1 and CB2), adenosine (A2A), and vanilloid (TRPV1) receptors, they also modulate PUFA metabolism within a wide variety of specialized lipid mediators that promote or resolve inflammation and oxidative stress. Clinical evidence reviewed in this study links PUFAs and cannabinoids to changes in ECS tone, immune function, metabolic and oxidative stress adaptation, and overall maintenance of a well-balanced systemic function of the body. Understanding how the body coordinates signals from the exogenous and endogenous ECS modulators is critical for discerning the underlying molecular mechanisms of the ECS tone in healthy and disease states. Nutritional and lifestyle interventions represent promising approaches to address chronic metabolic and inflammatory disorders that may overlap in the population at risk. Further investigation and validation of dietary interventions that modulate the ECS are required in order to devise clinically successful second-generation management strategies.
Keywords: ECS tone; inflammation resolution; oxidative stress; phytocannabinoids; systemic redox balance.
Conflict of interest statement
S.K. consulted and received research grants from Standard Process Inc. S.V., M.B., S.L.B.-B., C.C. and C.P. are employed by Standard Process Inc. J.P.T. served as VP Clinical Science for Standard Process Inc. C.W. and T.R. declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

