Extracellular Vesicles as Potential Therapeutics for Inflammatory Diseases
- PMID: 34067503
- PMCID: PMC8196952
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22115487
Extracellular Vesicles as Potential Therapeutics for Inflammatory Diseases
Abstract
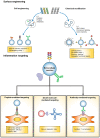
Extracellular vesicles (EV) deliver cargoes such as nucleic acids, proteins, and lipids between cells and serve as an intercellular communicator. As it is revealed that most of the functions associated to EVs are closely related to the immune response, the important role of EVs in inflammatory diseases is emerging. EVs can be functionalized through EV surface engineering and endow targeting moiety that allows for the target specificity for therapeutic applications in inflammatory diseases. Moreover, engineered EVs are considered as promising nanoparticles to develop personalized therapeutic carriers. In this review, we highlight the role of EVs in various inflammatory diseases, the application of EV as anti-inflammatory therapeutics, and the current state of the art in EV engineering techniques.
Keywords: EV engineering; biomarker; extracellular vesicle; inflammatory disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extracellular vesicle-based Nanotherapeutics: Emerging frontiers in anti-inflammatory therapy.Theranostics. 2020 Jul 9;10(18):8111-8129. doi: 10.7150/thno.47865. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32724461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicle-based therapeutics: Extracellular vesicles as therapeutic targets and agents.Pharmacol Ther. 2023 Feb;242:108352. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2023.108352. Epub 2023 Jan 23. Pharmacol Ther. 2023. PMID: 36702209 Review.
-
Hybrid Nanoparticle Engineered with Transforming Growth Factor -β1-Overexpressed Extracellular Vesicle and Cartilage-Targeted Anti-Inflammatory Liposome for Osteoarthritis.ACS Nano. 2024 Dec 17;18(50):33937-33952. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.4c07992. Epub 2024 Dec 8. ACS Nano. 2024. PMID: 39648484 Free PMC article.
-
Yin-Yang: two sides of extracellular vesicles in inflammatory diseases.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Aug 27;22(1):514. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02779-9. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39192300 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular-Vesicle-Based Therapeutics in Neuro-Ophthalmic Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 19;24(10):9006. doi: 10.3390/ijms24109006. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240353 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic potential of exosome-based personalized delivery platform in chronic inflammatory diseases.Asian J Pharm Sci. 2023 Jan;18(1):100772. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2022.100772. Epub 2022 Dec 31. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2023. PMID: 36896446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Updated View of the Importance of Vesicular Trafficking and Transport and Their Role in Immune-Mediated Diseases: Potential Therapeutic Interventions.Membranes (Basel). 2022 May 25;12(6):552. doi: 10.3390/membranes12060552. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35736259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Extracellular Vesicles from Ecklonia cava on 12-O-Tetradecanoylphorbol-13-Acetate-Induced Skin Inflammation in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 21;25(23):12522. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312522. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684233 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles in the Mesenchymal Stem Cell/Macrophage Axis: Potential Targets for Inflammatory Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 20;26(6):2827. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062827. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles and Their Mimetics: A Comparative Study of Their Pharmacological Activities and Immunogenicity Profiles.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Apr 20;15(4):1290. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15041290. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37111775 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

