Angiotensinergic Neurotransmissions in the Medial Amygdala Nucleus Modulate Behavioral Changes in the Forced Swimming Test Evoked by Acute Restraint Stress in Rats
- PMID: 34067508
- PMCID: PMC8156471
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10051217
Angiotensinergic Neurotransmissions in the Medial Amygdala Nucleus Modulate Behavioral Changes in the Forced Swimming Test Evoked by Acute Restraint Stress in Rats
Abstract
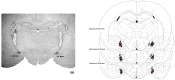
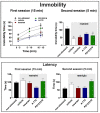
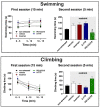
We investigated the role of angiotensin II type 1 (AT1 receptor) and type 2 (AT2 receptor) and MAS receptors present in the medial amygdaloid nucleus (MeA) in behavioral changes in the forced swimming test (FST) evoked by acute restraint stress in male rats. For this, rats received bilateral microinjection of either the selective AT1 receptor antagonist losartan, the selective AT2 receptor antagonist PD123319, the selective MAS receptor antagonist A-779, or vehicle 10 min before a 60 min restraint session. Then, behavior in the FST was evaluated immediately after the restraint (15 min session) and 24 h later (5 min session). The behavior in the FST of a non-stressed group was also evaluated. We observed that acute restraint stress decreased immobility during both sessions of the FST in animals treated with vehicle in the MeA. The decreased immobility during the first session was inhibited by intra-MeA administration of PD123319, whereas the effect during the second session was not identified in animals treated with A-779 into the MeA. Microinjection of PD123319 into the MeA also affected the pattern of active behaviors (i.e., swimming and climbing) during the second session of the FST. Taken together, these results indicate an involvement of angiotensinergic neurotransmissions within the MeA in behavioral changes in the FST evoked by stress.
Keywords: amygdala; angiotensin; depression; rodents; stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

