Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte Antigen-4 in Colorectal Cancer: Another Therapeutic Side of Capecitabine
- PMID: 34067631
- PMCID: PMC8155910
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13102414
Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte Antigen-4 in Colorectal Cancer: Another Therapeutic Side of Capecitabine
Abstract
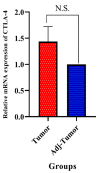
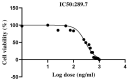
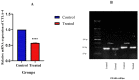
Cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4) is an inhibitory immune checkpoint that can be expressed in tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and colorectal cancer (CRC) cells. This immune checkpoint can attenuate anti-tumoral immune responses and facilitate tumor growth and metastasis. Although capecitabine is an effective chemotherapeutic agent for treating CRC, its effect on the tumoral CTLA-4 expression remains unclear. In the current research, we applied the GSE110224 and GSE25070 datasets to characterize CTLA-4 expression in CRC patients. Then, we analyzed CTLA-4 expression in CRC samples, HT-29, HCT-166, and SW480 cell lines using real-time PCR. Our bioinformatic results have highlighted the overexpression of CTLA-4 in the CRC tissues compared to the adjacent non-tumoral tissues. Our in vitro studies have indicated that SW480 cells can substantially overexpress CTLA-4 compared to HT-29 and HCT 116 cells. In addition, capecitabine can remarkably downregulate the expression of CTLA-4 in SW480 cells. Collectively, capecitabine can inhibit the expression of CTLA-4 in CRC cells and might bridge the immunotherapy approaches with chemotherapy.
Keywords: CTLA-4; capecitabine; chemotherapy; colorectal cancer; immune checkpoint; immune checkpoint inhibitors; immunotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Hosseinkhani N., Derakhshani A., Kooshkaki O., Abdoli Shadbad M., Hajiasgharzadeh K., Baghbanzadeh A., Safarpour H., Mokhtarzadeh A., Brunetti O., Yue S.C. Immune Checkpoints and CAR-T Cells: The Pioneers in Future Cancer Therapies? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020;21:8305. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218305. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

