Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis Reveals Hub Genes Contributing to Fuzz Development in Gossypium arboreum
- PMID: 34067654
- PMCID: PMC8156360
- DOI: 10.3390/genes12050753
Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis Reveals Hub Genes Contributing to Fuzz Development in Gossypium arboreum
Abstract
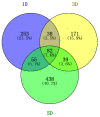
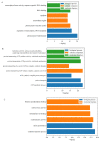
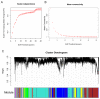
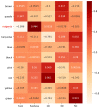
Fuzzless mutants are ideal materials to decipher the regulatory network and mechanism underlying fuzz initiation and formation. In this study, we utilized two Gossypium arboreum accessions differing in fuzz characteristics to explore expression pattern differences and discriminate genes involved in fuzz development using RNA sequencing. Gene ontology (GO) analysis was conducted and found that DEGs were mainly enriched in the regulation of transcription, metabolic processes and oxidation-reduction-related processes. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis discerned the MEmagenta module highly associated with a fuzz/fuzzless trait, which included a total of 50 hub genes differentially expressed between two materials. GaFZ, which negatively regulates trichome and fuzz formation, was found involved in MEmagenta cluster1. In addition, twenty-eight hub genes in MEmagenta cluster1 were significantly up-regulated and expressed in fuzzless mutant DPL972. It is noteworthy that Ga04G1219 and Ga04G1240, which, respectively, encode Fasciclin-like arabinogalactan protein 18(FLA18) and transport protein, showed remarkable differences of expression level and implied that they may be involved in protein glycosylation to regulate fuzz formation and development. This module and hub genes identified in this study will provide new insights on fiber and fuzz formation and be useful for the molecular design breeding of cotton genetic improvement.
Keywords: WGCNA; fuzz; hub genes; module; transcriptome analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis Reveals Hub Genes for Fuzz Development in Gossypium hirsutum.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jan 13;14(1):208. doi: 10.3390/genes14010208. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36672949 Free PMC article.
-
Large-fragment insertion activates gene GaFZ (Ga08G0121) and is associated with the fuzz and trichome reduction in cotton (Gossypium arboreum).Plant Biotechnol J. 2021 Jun;19(6):1110-1124. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13532. Epub 2021 Feb 7. Plant Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 33369825 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Identification and Transcriptome Analysis of Lintless and Fuzzless Traits in Gossypium arboreum L.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 29;21(5):1675. doi: 10.3390/ijms21051675. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32121400 Free PMC article.
-
Fine mapping and identification of the fuzzless gene GaFzl in DPL972 (Gossypium arboreum).Theor Appl Genet. 2019 Aug;132(8):2169-2179. doi: 10.1007/s00122-019-03330-3. Epub 2019 Apr 2. Theor Appl Genet. 2019. PMID: 30941465 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative proteomic analysis reveals differentially expressed proteins correlated with fuzz fiber initiation in diploid cotton (Gossypium arboreum L.).J Proteomics. 2013 Apr 26;82:113-29. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2013.02.020. Epub 2013 Mar 6. J Proteomics. 2013. PMID: 23474080
Cited by
-
Analysis of transcriptome data and quantitative trait loci enables the identification of candidate genes responsible for fiber strength in Gossypium barbadense.G3 (Bethesda). 2022 Aug 25;12(9):jkac167. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkac167. G3 (Bethesda). 2022. PMID: 35881688 Free PMC article.
-
Revealing Genetic Differences in Fiber Elongation between the Offspring of Sea Island Cotton and Upland Cotton Backcross Populations Based on Transcriptome and Weighted Gene Coexpression Networks.Genes (Basel). 2022 May 26;13(6):954. doi: 10.3390/genes13060954. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35741716 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Research and Plant Breeding.Genes (Basel). 2022 Dec 23;14(1):51. doi: 10.3390/genes14010051. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36672792 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of hub genes, lipid metabolism, and the immune microenvironment in stomach carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Aug;10(15):834. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-3530. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36034995 Free PMC article.
-
Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis Reveals Hub Genes for Fuzz Development in Gossypium hirsutum.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jan 13;14(1):208. doi: 10.3390/genes14010208. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36672949 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dai X., Zhou L., Zhang W., Cai L., Guo H., Tian H., Schiefelbein J., Wang S. A single amino acid substitution in the R3 domain of GLABRA1 leads to inhibition of trichome formation in Arabidopsis without affecting its interaction with GLABRA3. Plant Cell Environ. 2015;39:897–907. doi: 10.1111/pce.12695. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

