Comprehensive Transcriptome Analysis of Rare Carpinus putoensis Plants under NO2 stress
- PMID: 34067657
- PMCID: PMC8156095
- DOI: 10.3390/genes12050754
Comprehensive Transcriptome Analysis of Rare Carpinus putoensis Plants under NO2 stress
Abstract
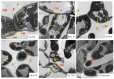
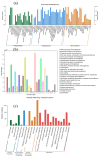
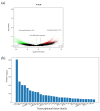
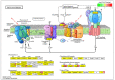
We evaluated a transcriptome using high-throughput Illumina HiSeq sequencing and related it to the morphology, leaf anatomy, and physiological parameters of Carpinus putoensis putoensis under NO2 stress. The molecular mechanism of the C. putoensis NO2 stress response was evaluated using sequencing data. NO2 stress adversely affected the morphology, leaf anatomy, and total peroxidase (POD) activity. Through RNA-seq analysis, we used NCBI to compare the transcripts with nine databases and obtained their functional annotations. We annotated up to 2255 million clean Illumina paired-end RNA-seq reads, and 250,200 unigene sequences were assembled based on the resulting transcriptome data. More than 89% of the C. putoensis transcripts were functionally annotated. Under NO2 stress, 1119 genes were upregulated and 1240 were downregulated. According to the KEGG pathway and GO analyses, photosynthesis, chloroplasts, plastids, and the stimulus response are related to NO2 stress. Additionally, NO2 stress changed the expression of POD families, and the HPL2, HPL1, and POD genes exhibited high expression. The transcriptome analysis of C. putoensis leaves under NO2 stress supplies a reference for studying the molecular mechanism of C. putoensis resistance to NO2 stress. The given transcriptome data represent a valuable resource for studies on plant genes, which will contribute towards genome annotations during future genome projects.
Keywords: NO2 stress; gene expression; high-throughput sequencing; molecular mechanism; resistance; transcriptome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Physiological and biochemical responses of two precious Carpinus species to high-concentration NO2 stress and their natural recovery.Sci Rep. 2021 May 4;11(1):9500. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84702-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33947881 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring drought stress-regulated genes in senna (Cassia angustifolia Vahl.): a transcriptomic approach.Funct Integr Genomics. 2017 Jan;17(1):1-25. doi: 10.1007/s10142-016-0523-y. Epub 2016 Oct 5. Funct Integr Genomics. 2017. PMID: 27709374
-
A chromosome-level reference genome of the hornbeam, Carpinus fangiana.Sci Data. 2020 Jan 21;7(1):24. doi: 10.1038/s41597-020-0370-5. Sci Data. 2020. PMID: 31964866 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive transcriptome analysis reveals genes in response to water deficit in the leaves of Saccharum narenga (Nees ex Steud.) hack.BMC Plant Biol. 2018 Oct 20;18(1):250. doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1428-9. BMC Plant Biol. 2018. PMID: 30342477 Free PMC article.
-
Deep sequencing-based characterization of transcriptome of Pyrus ussuriensis in response to cold stress.Gene. 2018 Jun 30;661:109-118. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.03.067. Epub 2018 Mar 23. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29580898
Cited by
-
Physiological and transcriptomic analyses reveal the regulatory mechanisms for the adaptation of Quercus robur to shade conditions.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Jul 2;25(1):821. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06843-w. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40604453 Free PMC article.
-
Acute NO2 Stress Shortens the Median Survival Period of Bougainvillea glabra 'Elizabeth Angus' by Disrupting Tissue Structure and Photosynthetic Response Centers.Plants (Basel). 2023 Nov 30;12(23):4028. doi: 10.3390/plants12234028. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38068663 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Investigation of Lipid Transfer Proteins Involved in Male Fertility and Other Biological Processes in Maize.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 14;24(2):1660. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021660. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36675174 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring potential polysaccharide utilization loci involved in the degradation of typical marine seaweed polysaccharides by Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron.Front Microbiol. 2024 May 9;15:1332105. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1332105. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38800758 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic mechanism of nitrogen modified atmosphere storage on delaying quality deterioration of rice grains.Food Chem X. 2022 Nov 19;16:100519. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2022.100519. eCollection 2022 Dec 30. Food Chem X. 2022. PMID: 36519102 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rahmat M., Maulina W., Rustami E., Azis M., Budiarti D., Seminar K., Yuwono A., Alatas H. Performance in real condition of photonic crystal sensor based NO2 gas monitoring system. Atmos. Environ. 2013;79:480–485. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2013.05.057. - DOI
-
- Sasakawa H., Yoneyama T. Transformation of atmospheric NO2 absorbed in spinach leaves. Plant Cell Physiol. 1979;20:263–266. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.pcp.a075801. - DOI
-
- Lu M., Li Y.J., Lu J.P. The study of greening trees on the atmospheric pollutant absorption ability. J. Urban. Environ. Urban. Ecol. 2002;15:7–9.
-
- Stulen I., Pérez-Soba M., de Kok L.J., van der Eerden L. Impact of gaseous nitrogen deposition on plant functioning. New Phytol. 1998;139:61–70. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-8137.1998.00179.x. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

