Effects of Daily Matcha and Caffeine Intake on Mild Acute Psychological Stress-Related Cognitive Function in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Study
- PMID: 34067795
- PMCID: PMC8156288
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13051700
Effects of Daily Matcha and Caffeine Intake on Mild Acute Psychological Stress-Related Cognitive Function in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Study
Abstract
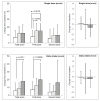
Matcha, a type of green tea, has a higher amino acid content than other types of tea. We previously examined the ability of matcha to improve cognitive function in older adults and determined that continuous matcha intake improves attention and executive function. This study aimed to compare the effects of matcha and caffeine and clarify the differences between these effects. The study was registered at the University Hospital Medical Information Network (UMIN000036578). The effect of single and continuous intake was compared, and the usefulness of continuous intake was evaluated under the stress condition. The Uchida-Kraepelin test (UKT) was used to induce mild acute stress, and the Cognitrax was used to evaluate cognitive function. A single dose of caffeine improved attentional function during or after stress loading. The reduced reaction time in the Cognitrax, observed following a single dose of matcha, was likely due to caffeine. The matcha group showed an increase in the amount of work after continuous intake, whereas the caffeine group only showed an increase in the amount of work for the UKT after a single dose. Ingesting matcha with caffeine improves both attention and work performance when suffering from psychological stress compared with caffeine alone.
Keywords: attention; caffeine; cognitive function; executive function; green tea; matcha; middle-aged and older adults; mild acute psychological stress; performance; randomized placebo-controlled trial.
Conflict of interest statement
Yoshitake Baba, Shun Inagaki, Sae Nakagawa, Makoto Kobayashi, and Takanobu Takihara are employees of ITO EN, LTD. HUMA R&D CORP. conducted participant recruitment, selection, allocation, observation, and data collection. Toshiyuki Kaneko was the doctor for this study and was contracted by HUMA R&D CORP. The study was properly implemented by a third party.
Figures
References
-
- Fredholm B.B., Bättig K., Holmén J., Nehlig A., Zvartau E.E. Actions of caffeine in the brain with special reference to factors that contribute to its widespread use. Pharmacol. Rev. 1999;51:83–133. - PubMed
-
- Kaster M.P., Machado N.J., Silva H.B., Nunes A., Ardais A.P., Santana M., Baqi Y., Müller C.E., Rodrigues A.L.S., Porciúncula L.O., et al. Caffeine acts through neuronal adenosine A 2A receptors to prevent mood and memory dysfunction triggered by chronic stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2015;112:7833–7838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1423088112. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

