Properties of WCCo Composites Produced by the SPS Method Intended for Cutting Tools for Machining of Wood-Based Materials
- PMID: 34067915
- PMCID: PMC8156679
- DOI: 10.3390/ma14102618
Properties of WCCo Composites Produced by the SPS Method Intended for Cutting Tools for Machining of Wood-Based Materials
Abstract
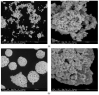
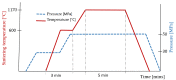
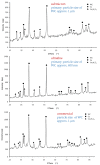
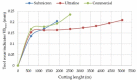
This paper presents the possibility of using the Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) method to obtain WCCo composite materials. Such materials are used as cutting blades for machining wood-based materials. Two series of composites, different in grain size and cobalt content, were analyzed in the paper. The produced materials were characterized using Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and tribological properties were determined. In addition, preliminary tests were carried out on the durability of the blades made of sintered WCCo composites while machining three-layer chipboard. The results of the microstructure analysis proved that the SPS method makes it possible to obtain solid composites. Phase analysis showed the occurrence of the following phases: WC, Co, and Co3W9C4. The lowest friction coefficient value was found in samples sintered using powder with an average primary particle size of 400 nm (ultrafine).
Keywords: Spark Plasma Sintering; cemented carbides WCCo; powder metallurgy; sintering.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
The Analysis of Erosive Wear Resistance of WC-Co Carbides Obtained by Spark Plasma Sintering Method.Materials (Basel). 2021 Nov 30;14(23):7326. doi: 10.3390/ma14237326. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34885479 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Diamond Grain Size on the Basic Properties of WC-Co/Diamond Composites Used in Tools for Wood-Based Materials Machining.Materials (Basel). 2022 May 17;15(10):3569. doi: 10.3390/ma15103569. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35629595 Free PMC article.
-
Spark Plasma Sintering of Fine-Grained WC-Co Composites.Materials (Basel). 2023 Dec 6;16(24):7526. doi: 10.3390/ma16247526. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38138668 Free PMC article.
-
Properties, Advantages, and Prospects of Using Cobalt-Free Composites Based on Tungsten Carbide in Industry.Materials (Basel). 2024 Dec 31;18(1):129. doi: 10.3390/ma18010129. Materials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39795774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights on Spark Plasma Sintering of Magnesium Composites: A Review.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Jun 24;12(13):2178. doi: 10.3390/nano12132178. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35808014 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Wear Characteristics of WC-Co Cutting Tools Obtained by the U-FAST Method During Particleboard Milling.Materials (Basel). 2025 Aug 21;18(16):3907. doi: 10.3390/ma18163907. Materials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40870224 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of Spark Plasma Sintering Technology by Taguchi Method in the Production of a Wide Range of Materials: Review.Materials (Basel). 2023 Aug 9;16(16):5539. doi: 10.3390/ma16165539. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37629830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Testing for Abrasion Resistance of WC-Co Composites for Blades Used in Wood-Based Material Processing.Materials (Basel). 2023 Aug 25;16(17):5836. doi: 10.3390/ma16175836. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37687529 Free PMC article.
-
The Analysis of Erosive Wear Resistance of WC-Co Carbides Obtained by Spark Plasma Sintering Method.Materials (Basel). 2021 Nov 30;14(23):7326. doi: 10.3390/ma14237326. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34885479 Free PMC article.
-
Surface Topography Description after Turning Inconel 718 with a Conventional, Wiper and Special Insert Made by the SPS Technique.Materials (Basel). 2023 Jan 19;16(3):949. doi: 10.3390/ma16030949. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36769960 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sommer M., Schubert W.D., Zobetz E., Warbichler P. On the formation of very large WC crystals during sintering of ultrafine WC–Co alloys. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2002;20:41–50. doi: 10.1016/S0263-4368(01)00069-5. - DOI
-
- Ban Z.G., Shaw L.L. Synthesis and processing of nanostructured WC-Co materials. J. Mater. Sci. 2002;37:3397–3403. doi: 10.1023/A:1016553426227. - DOI
-
- Kim H.C., Oh D.Y., Shon I.J. Sintering of nanophase WC–15vol.% Co hard metals by rapid sintering process. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2004;22:197–203. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2004.06.006. - DOI
-
- Raihanuzzaman R.M., Han S.T., Ghomashchi R., Kim H.S., Hong S.J. Conventional sintering of WC with nano-sized Co binder: Characterization and mechanical behavior. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2015;53:2–6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2015.04.033. - DOI
-
- Emanuelli L., Molinari A., Arrighetti G., Garoli G.T. Dependence of the Mechanical Properties on the Microstructural Parameters of WC-Co. Powder Metall. Prog. 2019;19:23–33. doi: 10.1515/pmp-2019-0003. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

