Polyamine Homeostasis in Development and Disease
- PMID: 34068137
- PMCID: PMC8162569
- DOI: 10.3390/medsci9020028
Polyamine Homeostasis in Development and Disease
Abstract
Polycationic polyamines are present in nearly all living organisms and are essential for mammalian cell growth and survival, and for development. These positively charged molecules are involved in a variety of essential biological processes, yet their underlying mechanisms of action are not fully understood. Several studies have shown both beneficial and detrimental effects of polyamines on human health. In cancer, polyamine metabolism is frequently dysregulated, and elevated polyamines have been shown to promote tumor growth and progression, suggesting that targeting polyamines is an attractive strategy for therapeutic intervention. In contrast, polyamines have also been shown to play critical roles in lifespan, cardiac health and in the development and function of the brain. Accordingly, a detailed understanding of mechanisms that control polyamine homeostasis in human health and disease is needed to develop safe and effective strategies for polyamine-targeted therapy.
Keywords: aging; cancer; development; metabolism; polyamines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funding sponsors had no role in the writing or the decision to publish this manuscript.
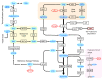
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

