Human Milk from Previously COVID-19-Infected Mothers: The Effect of Pasteurization on Specific Antibodies and Neutralization Capacity
- PMID: 34068142
- PMCID: PMC8152997
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13051645
Human Milk from Previously COVID-19-Infected Mothers: The Effect of Pasteurization on Specific Antibodies and Neutralization Capacity
Abstract
Background: Since the outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), many put their hopes in the rapid availability of effective immunizations. Human milk, containing antibodies against syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), may serve as means of protection through passive immunization. We aimed to determine the presence and pseudovirus neutralization capacity of SARS-CoV-2 specific IgA in human milk of mothers who recovered from COVID-19, and the effect of pasteurization on these antibodies.
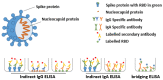
Methods: This prospective case control study included lactating mothers, recovered from (suspected) COVID-19 and healthy controls. Human milk and serum samples were collected. To assess the presence of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies we used multiple complementary assays, namely ELISA with the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein (specific for IgA and IgG), receptor binding domain (RBD) and nucleocapsid (N) protein for IgG in serum, and bridging ELISA with the SARS-CoV-2 RBD and N protein for specific Ig (IgG, IgM and IgA in human milk and serum). To assess the effect of pasteurization, human milk was exposed to Holder (HoP) and High Pressure Pasteurization (HPP).
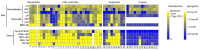
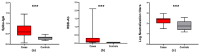
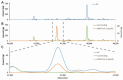
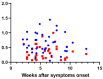
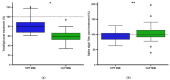
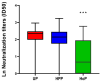
Results: Human milk contained abundant SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in 83% of the proven cases and in 67% of the suspected cases. Unpasteurized milk with and without these antibodies was found to be capable of neutralizing a pseudovirus of SARS-CoV-2 in (97% and 85% of the samples respectively). After pasteurization, total IgA antibody levels were affected by HoP, while SARS-CoV-2 specific antibody levels were affected by HPP. Pseudovirus neutralizing capacity of the human milk samples was only retained with the HPP approach. No correlation was observed between milk antibody levels and neutralization capacity.
Conclusions: Human milk from recovered COVID-19-infected mothers contains SARS-CoV-2 specific antibodies which maintained neutralization capacity after HPP. All together this may represent a safe and effective immunization strategy after HPP.
Keywords: COVID-19; breastfeeding; immunoglobulins; pasteurization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human Milk SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies up to 6 Months After Vaccination.Pediatrics. 2022 Feb 1;149(2):e2021054260. doi: 10.1542/peds.2021-054260. Pediatrics. 2022. PMID: 34981122 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2-Specific Antibodies' Binding Capacity Between Human Milk and Serum from Coronavirus Disease 2019-Recovered Women.Breastfeed Med. 2021 May;16(5):393-401. doi: 10.1089/bfm.2020.0381. Epub 2021 Apr 9. Breastfeed Med. 2021. PMID: 33835835
-
Functional Antibodies Against SARS-CoV-2 Receptor Binding Domain Variants with Mutations N501Y or E484K in Human Milk from COVID-19-Vaccinated, -Recovered, and -Unvaccinated Women.Breastfeed Med. 2022 Feb;17(2):163-172. doi: 10.1089/bfm.2021.0232. Epub 2021 Nov 22. Breastfeed Med. 2022. PMID: 34809492
-
Titres and neutralising capacity of SARS-CoV-2-specific antibodies in human milk: a systematic review.Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2022 Mar;107(2):174-180. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2021-322156. Epub 2021 Jul 13. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2022. PMID: 34257103
-
Neutralizing antibodies in milk and blood of lactating women vaccinated for SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review.Rev Paul Pediatr. 2024 Sep 6;43:e2023210. doi: 10.1590/1984-0462/2025/43/2023210. eCollection 2024. Rev Paul Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39258663 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Wellbeing of Breastfeeding Women in Australia and New Zealand during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Study.Nutrients. 2021 May 27;13(6):1831. doi: 10.3390/nu13061831. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34072039 Free PMC article.
-
Breastfeeding vs. breast milk transmission during COVID-19 pandemic, which is more important?Front Pediatr. 2023 Sep 6;11:1253333. doi: 10.3389/fped.2023.1253333. eCollection 2023. Front Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37744448 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibodies in breast milk: Pro-bodies designed for healthy newborn development.Immunol Rev. 2024 Nov;328(1):192-204. doi: 10.1111/imr.13411. Epub 2024 Oct 22. Immunol Rev. 2024. PMID: 39435770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic Analysis of Human Milk Reveals Nutritional and Immune Benefits in the Colostrum from Mothers with COVID-19.Nutrients. 2022 Jun 17;14(12):2513. doi: 10.3390/nu14122513. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35745243 Free PMC article.
-
Human Milk SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies up to 6 Months After Vaccination.Pediatrics. 2022 Feb 1;149(2):e2021054260. doi: 10.1542/peds.2021-054260. Pediatrics. 2022. PMID: 34981122 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

