Choline-Sigma-1R as an Additional Mechanism for Potentiation of Orexin by Cocaine
- PMID: 34068146
- PMCID: PMC8152999
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22105160
Choline-Sigma-1R as an Additional Mechanism for Potentiation of Orexin by Cocaine
Abstract
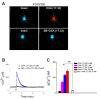
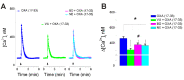
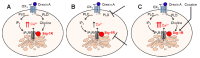
Orexin A, an endogenous peptide involved in several functions including reward, acts via activation of orexin receptors OX1 and OX2, Gq-coupled GPCRs. We examined the effect of a selective OX1 agonist, OXA (17-33) on cytosolic calcium concentration, [Ca2+]i, in neurons of nucleus accumbens, an important area in the reward circuit. OXA (17-33) increased [Ca2+]i in a dose-dependent manner; the effect was prevented by SB-334867, a selective OX1 receptors antagonist. In Ca2+-free saline, the OXA (17-33)-induced increase in [Ca2+]i was not affected by pretreatment with bafilomycin A1, an endo-lysosomal calcium disrupter, but was blocked by 2-APB and xestospongin C, antagonists of inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) receptors. Pretreatment with VU0155056, PLD inhibitor, or BD-1047 and NE-100, Sigma-1R antagonists, reduced the [Ca2+]i response elicited by OXA (17-33). Cocaine potentiated the increase in [Ca2+]i by OXA (17-33); the potentiation was abolished by Sigma-1R antagonists. Our results support an additional signaling mechanism for orexin A-OX1 via choline-Sigma-1R and a critical role for Sigma-1R in the cocaine-orexin A interaction in nucleus accumbens neurons.
Keywords: OX1 receptor; PLD; choline; orexin A; phospholipase D; reward.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of activation of nucleus accumbens neurons by cocaine via sigma-1 receptor-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-transient receptor potential canonical channel pathways.Cell Calcium. 2015 Aug;58(2):196-207. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2015.05.001. Epub 2015 May 27. Cell Calcium. 2015. PMID: 26077147 Free PMC article.
-
Orexin excites rat inferior vestibular nuclear neurons via co-activation of OX1 and OX 2 receptors.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2015 Jun;122(6):747-55. doi: 10.1007/s00702-014-1330-z. Epub 2014 Nov 5. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2015. PMID: 25371350
-
In vivo microdialysis reveals that blockade of accumbal orexin OX2 but not OX1 receptors enhances dopamine efflux in the nucleus accumbens of freely moving rats.Eur J Neurosci. 2022 Feb;55(3):733-745. doi: 10.1111/ejn.15593. Epub 2022 Jan 22. Eur J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 34989064
-
Orexin/Hypocretin Signaling.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2017;33:17-50. doi: 10.1007/7854_2016_49. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 27909990 Review.
-
Lipid signaling cascades of orexin/hypocretin receptors.Biochimie. 2014 Jan;96:158-65. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2013.06.015. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Biochimie. 2014. PMID: 23810911 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological Analysis of GABAA Receptor and Sigma1R Chaperone Interaction: Research Report I-Investigation of the Anxiolytic, Anticonvulsant and Hypnotic Effects of Allosteric GABAA Receptors' Ligands.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 31;24(11):9580. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119580. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298532 Free PMC article.
-
Orexin/hypocretin system dysfunction in patients with Takotsubo syndrome: A novel pathophysiological explanation.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Nov 3;9:1016369. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.1016369. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36407467 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of a dual orexin receptor antagonist on Alzheimer's disease: Sleep disorders and cognition.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Feb 1;9:984227. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.984227. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36816725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Choline-An Essential Nutrient with Health Benefits and a Signaling Molecule.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 24;26(15):7159. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157159. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroanatomical Basis for the Orexinergic Modulation of Anesthesia Arousal and Pain Control.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Apr 26;16:891631. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.891631. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35558876 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sakurai T., Amemiya A., Ishii M., Matsuzaki I., Chemelli R.M., Tanaka H., Williams S.C., Richardson J.A., Kozlowski G.P., Wilson S., et al. Orexins and orexin receptors: A family of hypothalamic neuropeptides and G protein-coupled receptors that regulate feeding behavior. Cell. 1998;92:573–585. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80949-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- de Lecea L., Kilduff T.S., Peyron C., Gao X., Foye P.E., Danielson P.E., Fukuhara C., Battenberg E.L., Gautvik V.T., Bartlett F.S., et al. The hypocretins: Hypothalamus-specific peptides with neuroexcitatory activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1998;95:322–327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.1.322. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Haghparast A., Fatahi Z., Arezoomandan R., Karimi S., Taslimi Z., Zarrabian S. Functional roles of orexin/hypocretin receptors in reward circuit. Prog. Brain Res. 2017;235:139–154. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

