Astragaloside IV Suppresses Hepatic Proliferation in Regenerating Rat Liver after 70% Partial Hepatectomy via Down-Regulation of Cell Cycle Pathway and DNA Replication
- PMID: 34068164
- PMCID: PMC8152973
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26102895
Astragaloside IV Suppresses Hepatic Proliferation in Regenerating Rat Liver after 70% Partial Hepatectomy via Down-Regulation of Cell Cycle Pathway and DNA Replication
Abstract
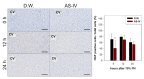
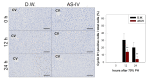
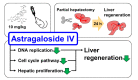
Astragaloside IV (AS-IV) is one of the major bio-active ingredients of huang qi which is the dried root of Astragalus membranaceus (a traditional Chinese medicinal plant). The pharmacological effects of AS-IV, including anti-oxidative, anti-cancer, and anti-diabetic effects have been actively studied, however, the effects of AS-IV on liver regeneration have not yet been fully described. Thus, the aim of this study was to explore the effects of AS-IV on regenerating liver after 70% partial hepatectomy (PHx) in rats. Differentially expressed mRNAs, proliferative marker and growth factors were analyzed. AS-IV (10 mg/kg) was administrated orally 2 h before surgery. We found 20 core genes showed effects of AS-IV, many of which were involved with functions related to DNA replication during cell division. AS-IV down-regulates MAPK signaling, PI3/Akt signaling, and cell cycle pathway. Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and cyclin D1 expression were also decreased by AS-IV administration. Transforming growth factor β1 (TGFβ1, growth regulation signal) was slightly increased. In short, AS-IV down-regulated proliferative signals and genes related to DNA replication. In conclusion, AS-IV showed anti-proliferative activity in regenerating liver tissue after 70% PHx.
Keywords: 70% partial hepatectomy; Astragali Radix; Astragalus membranaceus; astragaloside IV; huang qi; liver; liver regeneration; proliferation; rat.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Astragaloside IV and cycloastragenol promote liver regeneration through regulation of hepatic oxidative homeostasis and glucose/lipid metabolism.Phytomedicine. 2024 Dec;135:156165. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156165. Epub 2024 Oct 20. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39461202
-
Ursolic acid enhances mouse liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy.Pharm Biol. 2012 Apr;50(4):523-8. doi: 10.3109/13880209.2011.611143. Epub 2011 Dec 2. Pharm Biol. 2012. PMID: 22136205
-
Hepatocyte-specific deletion of farnesoid X receptor delays but does not inhibit liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy in mice.Hepatology. 2012 Dec;56(6):2344-52. doi: 10.1002/hep.25918. Hepatology. 2012. PMID: 22730081 Free PMC article.
-
Astragaloside IV derived from Astragalus membranaceus: A research review on the pharmacological effects.Adv Pharmacol. 2020;87:89-112. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2019.08.002. Epub 2019 Dec 18. Adv Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32089240 Review.
-
Pharmacological Effects of Astragaloside IV: A Review.Molecules. 2023 Aug 18;28(16):6118. doi: 10.3390/molecules28166118. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37630371 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Roles and Mechanisms of Astragaloside IV in Combating Neuronal Aging.Aging Dis. 2022 Dec 1;13(6):1845-1861. doi: 10.14336/AD.2022.0126. eCollection 2022 Dec 1. Aging Dis. 2022. PMID: 36465185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective Effect of Astragaloside IV against Cadmium-Induced Damage on Mouse Renal Podocytes (MPC5).Molecules. 2023 Jun 21;28(13):4897. doi: 10.3390/molecules28134897. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37446560 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

