Dietary Derived Propionate Regulates Pathogenic Fibroblast Function and Ameliorates Experimental Arthritis and Inflammatory Tissue Priming
- PMID: 34068191
- PMCID: PMC8152983
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13051643
Dietary Derived Propionate Regulates Pathogenic Fibroblast Function and Ameliorates Experimental Arthritis and Inflammatory Tissue Priming
Abstract
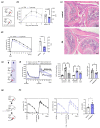
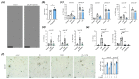
Short-chain fatty acids are gut-bacteria-derived metabolites that execute important regulatory functions on adaptive immune responses, yet their influence on inflammation driven by innate immunity remains understudied. Here, we show that propionate treatment in drinking water or upon local application into the joint reduced experimental arthritis and lowered inflammatory tissue priming mediated by synovial fibroblasts. On a cellular level, incubation of synovial fibroblasts with propionate or a physiological mixture of short-chain fatty acids interfered with production of inflammatory mediators and migration and induced immune-regulatory fibroblast senescence. Our study suggests that propionate mediates its alleviating effect on arthritis by direct abrogation of local arthritogenic fibroblast function.
Keywords: arthritis; cellular senescence; diet; inflammatory tissue priming; propionate; synovial fibroblasts.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Trompette A., Gollwitzer E.S., Yadava K., Sichelstiel A.K., Sprenger N., Ngom-Bru C., Blanchard C., Jut T., Nicod L.P., Harris N.L., et al. Gut microbiota metabolism of dietary fiber influences allergic airway disease and hematopoiesis. Nat. Med. 2014;20:159–166. doi: 10.1038/nm.3444. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zaiss M.M., Rapin A., Lebon L., Dubey L.K., Mosconi I., Sarter K., Piersigilli A., Menin L., Walker A.W., Rougemont J., et al. The Intestinal Microbiota Contributes to the Ability of Helminths to Modulate Allergic Inflammation. Immunity. 2015;43:998–1010. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.09.012. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

