Melatonin Successfully Rescues the Hippocampal Molecular Machinery and Enhances Anti-oxidative Activity Following Early-Life Sleep Deprivation Injury
- PMID: 34068192
- PMCID: PMC8153000
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox10050774
Melatonin Successfully Rescues the Hippocampal Molecular Machinery and Enhances Anti-oxidative Activity Following Early-Life Sleep Deprivation Injury
Abstract
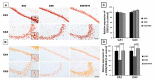
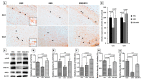
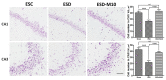
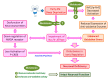
Early-life sleep deprivation (ESD) is a serious condition with severe cognitive sequelae. Considering hippocampus plays an essential role in cognitive regulation, the present study aims to determine whether melatonin, a neuroendocrine beard with significant anti-oxidative activity, would greatly depress the hippocampal oxidative stress, improves the molecular machinery, and consequently exerts the neuro-protective effects following ESD. Male weanling Wistar rats (postnatal day 21) were subjected to ESD for three weeks. During this period, the animals were administered normal saline or melatonin (10 mg/kg) via intraperitoneal injection between 09:00 and 09:30 daily. After three cycles of ESD, the animals were kept under normal sleep/wake cycle until they reached adulthood and were sacrificed. The results indicated that ESD causes long-term effects, such as impairment of ionic distribution, interruption of the expressions of neurotransmitters and receptors, decreases in the levels of several antioxidant enzymes, and impairment of several signaling pathways, which contribute to neuronal death in hippocampal regions. Melatonin administration during ESD prevented these effects. Quantitative evaluation of cells also revealed a higher number of neurons in the melatonin-treated animals when compared with the saline-treated animals. As the hippocampus is critical to cognitive activity, preserving or even improving the hippocampal molecular machinery by melatonin during ESD not only helps us to better understand the underlying mechanisms of ESD-induced neuronal dysfunction, but also the therapeutic use of melatonin to counteract ESD-induced neuronal deficiency.
Keywords: TOF-SIMS analysis; early-life sleep deprivation; hippocampus; melatonin; neurochemical expression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Early-life sleep deprivation persistently depresses melatonin production and bio-energetics of the pineal gland: potential implications for the development of metabolic deficiency.Brain Struct Funct. 2015 Mar;220(2):663-76. doi: 10.1007/s00429-014-0716-x. Epub 2014 Feb 11. Brain Struct Funct. 2015. PMID: 24515890
-
Melatonin ameliorates cognitive impairment induced by sleep deprivation in rats: role of oxidative stress, BDNF and CaMKII.Behav Brain Res. 2013 Nov 1;256:72-81. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2013.07.051. Epub 2013 Aug 6. Behav Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23933144
-
Melatonin successfully rescues hippocampal bioenergetics and improves cognitive function following drug intoxication by promoting Nrf2-ARE signaling activity.J Pineal Res. 2017 Sep;63(2). doi: 10.1111/jpi.12417. Epub 2017 May 25. J Pineal Res. 2017. PMID: 28480587
-
Melatonin preserves longevity protein (sirtuin 1) expression in the hippocampus of total sleep-deprived rats.J Pineal Res. 2009 Oct;47(3):211-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2009.00704.x. Epub 2009 Jul 21. J Pineal Res. 2009. PMID: 19627456
-
The use of chronobiotics in the resynchronization of the sleep/wake cycle. Therapeutical application in the early phases of Alzheimer's disease.Recent Pat Endocr Metab Immune Drug Discov. 2011 May;5(2):80-90. doi: 10.2174/187221411799015354. Recent Pat Endocr Metab Immune Drug Discov. 2011. PMID: 22074583 Review.
Cited by
-
Melatonin modulates TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway to ameliorate cognitive impairment in sleep-deprived rats.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 19;15:1430599. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1430599. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39101143 Free PMC article.
-
Lonicerae Japonicae Flos Extract Promotes Sleep in Sleep-Deprived and Lipopolysaccharide-Challenged Mice.Front Neurosci. 2022 Apr 12;16:848588. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.848588. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35495054 Free PMC article.
-
Sleep Deprivation-Induced Oxidative Stress in Rat Models: A Scoping Systematic Review.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Aug 11;12(8):1600. doi: 10.3390/antiox12081600. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37627596 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Effects of Cornelian Cherry Fruit (Cornus mas L.) Extract on Sleep Deprivation-Induced Oxidative Stress, Cytokine Dysregulation, and Behavioural Changes in Wistar Rats.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 May 28;47(6):399. doi: 10.3390/cimb47060399. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40699798 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomics and network analysis reveal the mechanism of Salvia miltiorrhiza bunge extract in ameliorating cognitive dysfunction in sleep-deprived rats.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 7;15(1):28873. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-14303-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40775015 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sleep in America Poll-Children and Sleep. [(accessed on 14 February 2021)];National Sleep Fundation. 2004 Available online: http://www.sleepfoundation.org/article/sleep-america-polls/2004-children....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

