Accuracy of a Novel SARS-CoV-2 Antigen-Detecting Rapid Diagnostic Test from Standardized Self-Collected Anterior Nasal Swabs
- PMID: 34068236
- PMCID: PMC8153114
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10102099
Accuracy of a Novel SARS-CoV-2 Antigen-Detecting Rapid Diagnostic Test from Standardized Self-Collected Anterior Nasal Swabs
Abstract
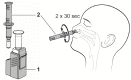
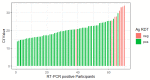
Background Antigen-detecting rapid diagnostic tests (Ag-RDT) for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) offer new opportunities for the quick and laboratory-independent identification of infected individuals for control of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. Despite the potential benefits, nasopharyngeal sample collection is frequently perceived as uncomfortable by patients and requires trained healthcare personnel with protective equipment. Therefore, anterior nasal self-sampling is increasingly recognized as a valuable alternative. Methods We performed a prospective, single-center, point of care validation of an Ag-RDT using a polypropylene absorbent collector for standardized self-collected anterior nasal swabs. Real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) from combined oropharyngeal/nasopharyngeal swabs served as a comparator. Primary endpoint was sensitivity of the standardized Ag-RDT in symptomatic patients with medium or high viral concentration (≥1 million RNA copies on RT-PCR for SARS-CoV-2). Results Between 12 February and 22 March 2021, 388 participants were enrolled. After exclusion of 9 patients for which no PCR result could be obtained, the novel Ag-RDT was evaluated based on 379 participants, of whom 273 were symptomatic and 106 asymptomatic. In 61 samples from symptomatic patients with medium or high viral load (≥1 million RNA copies), the sensitivity of the standardized Ag-RDT was 96.7% (59/61; 95% confidence interval (CI): 88.7-99.6%) for the primary endpoint. In total, 62 positive Ag-RDT results were detected out of 70 RT-PCR positive individuals, yielding an overall sensitivity of 88.6% (95% CI: 78.7-94.9%). Specificity was 99.7% (95% CI: 98.2-100%) in 309 RT-PCR negative individuals. Conclusions Here, we present a validation of a novel Ag-RDT with a standardized sampling process for anterior nasal self-collection, which meets World Health Organisation (WHO) criteria of ≥80% sensitivity and ≥97% specificity. Although less sensitive than RT-PCR, this assay could be beneficial due to its rapid results, ease of use, and suitability for standardized self-testing.
Keywords: COVID-19; COVID-19 diagnostic testing; SARS-COV-2 antigen testing; SARS-CoV-2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
References
-
- Foundation of Innovative New Diagnostics (FIND) SARS-COV-2 Diagnostics Pipeline. [(accessed on 13 May 2021)]; Available online: http://www.finddx.org/covid-19/pipeline/
-
- SARS-CoV-2 Antigen-Detecting Rapid Diagnostic Tests: An Implementation Guide. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2020.
-
- Lambert-Niclot S., Cuffel A., Le Pape S., Vauloup-Fellous C., Morand-Joubert L., Roque-Afonso A.-M., Le Goff J., Delaugerre C. Evaluation of a Rapid Diagnostic Assay for Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antigen in Nasopharyngeal Swabs. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020;58 doi: 10.1128/JCM.00977-20. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lindner A.K., Nikolai O., Kausch F., Wintel M., Hommes F., Gertler M., Krüger L.J., Gaeddert M., Tobian F., Lainati F., et al. Head-to-head comparison of SARS-CoV-2 antigen-detecting rapid test with self-collected nasal swab versus professional-collected nasopharyngeal swab. Eur. Respir. J. 2021;57:2003961. doi: 10.1183/13993003.03961-2020. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nagura-Ikeda M., Imai K., Tabata S., Miyoshi K., Murahara N., Mizuno T., Horiuchi M., Kato K., Imoto Y., Iwata M., et al. Clinical Evaluation of Self-Collected Saliva by Quantitative Reverse Transcription-PCR (RT-qPCR), Direct RT-qPCR, Reverse Transcription–Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification, and a Rapid Antigen Test To Diagnose COVID-19. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020;58 doi: 10.1128/JCM.01438-20. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

