Selection of Potential Yeast Probiotics and a Cell Factory for Xylitol or Acid Production from Honeybee Samples
- PMID: 34068237
- PMCID: PMC8153147
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo11050312
Selection of Potential Yeast Probiotics and a Cell Factory for Xylitol or Acid Production from Honeybee Samples
Abstract
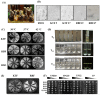
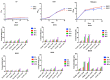
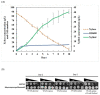
Excessive use of antibiotics has detrimental consequences, including antibiotic resistance and gut microbiome destruction. Probiotic-rich diets help to restore good microbes, keeping the body healthy and preventing the onset of chronic diseases. Honey contains not only prebiotic oligosaccharides but, like yogurt and fermented foods, is an innovative natural source for probiotic discovery. Here, a collection of three honeybee samples was screened for yeast strains, aiming to characterize their potential in vitro probiotic properties and the ability to produce valuable metabolites. Ninety-four isolates out of one-hundred and four were able to grow at temperatures of 30 °C and 37 °C, while twelve isolates could grow at 42 °C. Fifty-eight and four isolates displayed the ability to grow under stimulated gastrointestinal condition, at pH 2.0-2.5, 0.3% (w/v) bile salt, and 37 °C. Twenty-four isolates showed high autoaggregation of 80-100% and could utilize various sugars, including galactose and xylose. The cell count of these isolates (7-9 log cfu/mL) was recorded and stable during 6 months of storage. Genomic characterization based on the internal transcribed spacer region (ITS) also identified four isolates of Saccharomyces cerevisiae displayed good ability to produce antimicrobial acids. These results provided the basis for selecting four natural yeast isolates as starter cultures for potential probiotic application in functional foods and animal feed. Additionally, these S. cerevisiae isolates also produced high levels of acids from fermented sugarcane molasses, an abundant agricultural waste product from the sugar industry. Furthermore, one of ten identified isolates of Meyerozyma guilliermondiii displayed an excellent ability to produce a pentose sugar xylitol at a yield of 0.490 g/g of consumed xylose. Potentially, yeast isolates of honeybee samples may offer various biotechnological advantages as probiotics or metabolite producers of multiproduct-based lignocellulosic biorefinery.
Keywords: acid production; functional food; honey; probiotics; xylitol; yeast.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Technological properties and probiotic potential of yeasts isolated from traditional low-salt fermented Chinese fish Suan yu.J Food Biochem. 2019 Aug;43(8):e12865. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.12865. Epub 2019 Jun 4. J Food Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31368569
-
Probiotic potential of yeasts isolated from pineapple and their use in the elaboration of potentially functional fermented beverages.Food Res Int. 2018 May;107:518-527. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.02.054. Epub 2018 Feb 27. Food Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29580515
-
Probiotic and Functional Attributes of Yeasts Isolated from Different Traditional Fermented Foods and Products.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024 Aug 24. doi: 10.1007/s12602-024-10342-z. Online ahead of print. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024. PMID: 39180663
-
Exceptional hexose-fermenting ability of the xylitol-producing yeast Candida guilliermondii FTI 20037.J Biosci Bioeng. 2016 Jun;121(6):631-637. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2015.10.011. Epub 2015 Nov 18. J Biosci Bioeng. 2016. PMID: 26596373
-
Improving the drying of Propionibacterium freudenreichii starter cultures.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 May;105(9):3485-3494. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11273-3. Epub 2021 Apr 22. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33885925 Review.
Cited by
-
Schwanniomyces etchellsii, acid-thermotolerant yeasts from urban city soil.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Apr 17;39(6):159. doi: 10.1007/s11274-023-03602-7. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37067620
-
Biocontrol and Probiotic Function of Non-Saccharomyces Yeasts: New Insights in Agri-Food Industry.Microorganisms. 2023 May 30;11(6):1450. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11061450. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37374952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Honey microbiota, methods for determining the microbiological composition and the antimicrobial effect of honey - A review.Food Chem X. 2024 Jun 4;23:101524. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2024.101524. eCollection 2024 Oct 30. Food Chem X. 2024. PMID: 38947342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling the overlooked fungi: the vital of gut fungi in inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal cancer.Gut Pathog. 2024 Oct 15;16(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s13099-024-00651-7. Gut Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39407244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated omic analysis of a new flavor yeast strain in fermented rice milk.FEMS Yeast Res. 2025 Jan 30;25:foaf017. doi: 10.1093/femsyr/foaf017. FEMS Yeast Res. 2025. PMID: 40153366 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Srinivas B., Rani G.S., Kumar B.K., Chandrasekhar B., Krishna K.V., Devi T.A., Bhima B. Evaluating The Probiotic And Therapeutic Potentials Of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Strain (Obs2) Isolated From Fermented Nectar Of Toddy Palm. AMB Express. 2017;7:2. doi: 10.1186/s13568-016-0301-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

