Dietetic Students' Drivers and Barriers to Healthy Eating While Studying to Be a Healthcare Professional (a Pilot Study)
- PMID: 34068242
- PMCID: PMC8153143
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare9050579
Dietetic Students' Drivers and Barriers to Healthy Eating While Studying to Be a Healthcare Professional (a Pilot Study)
Abstract
Background: For Dietetics students, starting university means developing the knowledge and skills required to be a healthcare practitioner. This pilot study aimed to explore the perceptions and views of the students on their drivers and barriers of healthy eating while studying Dietetics at university.
Methods: A qualitative study was undertaken with a purposive sample of six final year Dietetic students at a UK university. Semi-structured in-depth interviews were used to elicit students' experiences and perceptions of barriers to healthy eating. Interview data were analysed thematically.
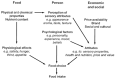
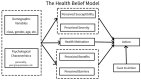
Results: Five themes emerged from the interview data including studying Dietetics, placement, influence of significant others, food security, and social and cultural aspects of the university life, with several sub-themes, and perspectives about the future beyond the university life.
Conclusions: The findings suggest a potential need for Dietetics course providers to consider the range of barriers to healthy eating that students may encounter whilst studying and how these may undermine their ability to develop healthy eating practices and effective professional skills. Further research is required that explores the extent of barriers to healthy eating and examine whether these impinge upon effective practice.
Keywords: barriers; dietetic students; drivers; food choice; healthy eating; qualitative.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exploring perceived training and professional development needs of Australian dietetic students and practising dietitians in the area of eating disorders: a focus group study.J Eat Disord. 2022 Mar 18;10(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s40337-022-00567-0. J Eat Disord. 2022. PMID: 35303959 Free PMC article.
-
'Oh God, I Have to Eat Something, But Where Can I Get Something Quickly?'-A Qualitative Interview Study on Barriers to Healthy Eating among University Students in Germany.Nutrients. 2019 Oct 14;11(10):2440. doi: 10.3390/nu11102440. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31614957 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the perceived influence of social media use on disordered eating in nutrition and dietetics students.J Hum Nutr Diet. 2023 Oct;36(5):2050-2059. doi: 10.1111/jhn.13212. Epub 2023 Jul 20. J Hum Nutr Diet. 2023. PMID: 37475206
-
A Review of Eating Disorders and Disordered Eating amongst Nutrition Students and Dietetic Professionals.Can J Diet Pract Res. 2015 Mar;76(1):38-43. doi: 10.3148/cjdpr-2014-031. Can J Diet Pract Res. 2015. PMID: 26067246 Review.
-
Dietetics students' experiences of dietetics workforce preparation and preparedness: a systematic review and qualitative synthesis.J Hum Nutr Diet. 2019 Apr;32(2):226-246. doi: 10.1111/jhn.12600. Epub 2018 Oct 16. J Hum Nutr Diet. 2019. PMID: 30328172
Cited by
-
Medical students' dietary habits: Motivations and barriers to reaching health goals.J Family Med Prim Care. 2024 May;13(5):1739-1746. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_1016_23. Epub 2024 May 24. J Family Med Prim Care. 2024. PMID: 38948602 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eves A., Kipps M., Parlett G. Undernourished students–myth or reality? Nutr. Food Sci. 1995;95:5–11. doi: 10.1108/00346659510078231. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

