Performance Evaluation of the Chinese Healthcare System
- PMID: 34068324
- PMCID: PMC8153293
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18105193
Performance Evaluation of the Chinese Healthcare System
Abstract
This study aims to evaluate the performance of the Chinese healthcare system. It uses sustainable development goal (SDG) 3, set by the United Nations to ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages as a benchmark. It uses data of 17 variables ranging from the year 2000 to 2017 and uses a multistage methodology to evaluate the performance. In the first stage, it uses difference in mean test to know whether or not the indicators show an improvement in the second decade of the 21st century compared to the first decade. In the second phase, simple linear regression has been used to know the rate of change of performance of every indicator over the sample period. The third step compares the performance of the healthcare sector with the sustainable goals set by the UN and the fourth phase attempts to forecast performance for the next five years i.e., 2018 to 2022. As per the results, the Chinese healthcare sector has performed very well on many fronts except alcohol consumption in males, road accidents and the incidence of non-communicable diseases. Alcohol consumption by males is touching dangerous levels. Therefore, the policies should focus on educating males to lower their alcohol consumption to stay fit and healthy.
Keywords: Chinese healthcare system; evaluation; performance; sustainable development goals (SDGs).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
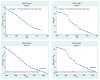
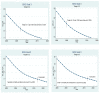



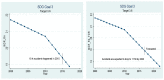

References
-
- UN Millennium Project . Investing in Development: A Practical Plan to Achieve the Millennium Development Goals. United Nations; New York, NY, USA: 2005.
-
- World Health Organization World Health Statistics, Geneva: World Health Organization. [(accessed on 23 December 2018)];2015 Available online: https://www.who.int/gho/publications/world_health_statistics/2015/en/
-
- Horton R. Offline: Why the Sustainable Development Goals will fail. Lancet. 2014;383:2196. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61046-1. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

