Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Stereotactic Ablative Body Radiotherapy for the Treatment of Oligometastatic Tumors versus Standard of Care
- PMID: 34068400
- PMCID: PMC8161824
- DOI: 10.3390/curroncol28030172
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Stereotactic Ablative Body Radiotherapy for the Treatment of Oligometastatic Tumors versus Standard of Care
Abstract
Background: Recent clinical trial results reported that stereotactic radiotherapy (SABR) may improve survival for patients with oligometastatic (OM) cancer. Given that these results come from a phase II trial, there remains considerable uncertainty about this finding, and about the cost-effectiveness of SABR for patients with OM cancer. In this analysis, we estimate the cost-effectiveness of SABR for oligometastatic cancer patients.
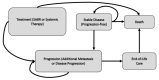
Methods: A probabilistic time-dependent Markov model was constructed to simulate treatment of oligometastatic cancer patients over five- and ten-year time horizons. The primary data source was the phase II, Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy for the Comprehensive Treatment of Oligometastases (SABR-COMET )trial and supplemented with data from the literature. We estimated the effect of SABR and the standard of care (SoC) using quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs). Costs were measured from a provincial payer perspective (2018 Canadian dollars).
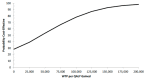
Results: In the reference case analysis (five-year time horizon), SABR was associated with additional incremental costs of CAD 38,487 and an incremental QALY gain of 0.84. This resulted in an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) of CAD 45,726 per QALY gained. Over a ten-year time horizon, the increased uncertainty in the long-term effectiveness of SABR resulted in an ICER of CAD 291,544 per QALY gained. Estimates from the probabilistic analysis indicated that at a willingness-to-pay (WTP) threshold of CAD 50,000 and CAD 100,000 per QALY gained, there is 54% and 78% probability (respectively) that SABR would be cost-effective using the five-year time horizon.
Conclusions: The adoption of SABR therapy requires a considerable upfront capital investment. Our results suggest that the cost-effectiveness of SABR is contingent on the uncertainty in the evidence base. Further clinical trials to confirm the effectiveness of SABR and research into the real-world costs associated with this treatment could reduce the uncertainty around implementation of the technology.
Keywords: SABR; cost-effectiveness analysis; cost-utility analysis; early health technology assessment; economic evaluation; health technology assessment; radiotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
We have read and understood
Figures
Comment in
-
The Cost-Effectiveness of Consolidative Radiation Therapy in Oligometastatic Disease: High-Value Proposition or Wishful Thinking?Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2022 Dec 1;114(5):824-826. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2022.09.016. Epub 2022 Nov 14. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2022. PMID: 36395796 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Stereotactic Ablative Radiation Therapy in Patients With Oligometastatic Cancer.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021 Apr 1;109(5):1185-1194. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2020.09.045. Epub 2020 Sep 28. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021. PMID: 33002541
-
Is SABR Cost-Effective in Oligometastatic Cancer? An Economic Analysis of the SABR-COMET Randomized Trial.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021 Apr 1;109(5):1176-1184. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2020.12.001. Epub 2020 Dec 10. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021. PMID: 33309977
-
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Local Treatment in Oligometastatic Disease.Front Oncol. 2021 Jun 15;11:667993. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.667993. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34211842 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-gene Pharmacogenomic Testing That Includes Decision-Support Tools to Guide Medication Selection for Major Depression: A Health Technology Assessment.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2021 Aug 12;21(13):1-214. eCollection 2021. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2021. PMID: 34484487 Free PMC article.
-
Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for Treatment-Resistant Depression: An Economic Analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2016 Mar 1;16(6):1-51. eCollection 2016. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2016. PMID: 27110317 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of Patient-Reported Outcome Differences by Radiotherapy Techniques for Bone Metastases in A Population-Based Healthcare System.Curr Oncol. 2022 Mar 18;29(3):2073-2080. doi: 10.3390/curroncol29030167. Curr Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35323367 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Review of Real-World Cost-Effectiveness Analyses of Cancer Interventions in Canada.Curr Oncol. 2022 Sep 30;29(10):7285-7304. doi: 10.3390/curroncol29100574. Curr Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36290851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stereotactic body radiotherapy as metastasis-directed therapy in oligometastatic prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Radiat Oncol. 2024 Dec 17;19(1):173. doi: 10.1186/s13014-024-02559-7. Radiat Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39690404 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Potters L., Kavanagh B., Galvin J.M., Hevezi J.M., Janjan N.A., Larson D.A., Mehta M.P., Ryu S., Steinberg M., Timmerman R., et al. American society for therapeutic radiology and oncology (ASTRO) and American college of radiology (ACR) practice guideline for the performance of stereotactic body radiation therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010;76:326–332. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.09.042. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Choy H. SABR as First Line Treatment Option. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017;12:S1661. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2017.09.189. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

