Contamination of Foods from Cameroon with Residues of 20 Halogenated Pesticides, and Health Risk of Adult Human Dietary Exposure
- PMID: 34068747
- PMCID: PMC8126213
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18095043
Contamination of Foods from Cameroon with Residues of 20 Halogenated Pesticides, and Health Risk of Adult Human Dietary Exposure
Abstract
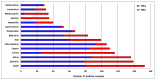
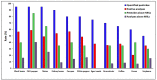
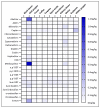
(1) Background: Halogenated pesticides are abundantly used in Cameroon, but there is no information on the health risk of consumers from exposure to their residues in foods. (2) Methods: Residues of 20 halogenated pesticides were determined in 11 agricultural products collected in the 3 largest cities of Cameroon using QuEChERS extraction and gas chromatography with electron capture detector (GC-ECD), and health risk from dietary exposure was assessed. (3) Results: Organochlorines pesticides aldrin, p,p'-dichlorodiphenyl-trichloroethane (DDT) and β-hexachlorocyclohexane (β-HCH) found in 85.0%, 81.9% and 72.5% of samples, respectively, were the most frequently detected. The highest average concentrations of residues were 1.12, 0.74 and 0.39 mg/kg for methoxychlor, alachlor and β-HCH, respectively, found in chilli pepper. Chili pepper (58.9%), cowpea (56.8%), black beans (56.5%) and kidney beans (54.0%) exhibited the highest residue occurrences. Levels above the European Union maximum residue limits (MRLs) were found for all the 20 pesticides, in 40.1% of the positive analyses, and the food samples contained 14 pesticides banned in Cameroon. Chronic, acute, cumulative and carcinogenic risk assessments revealed that lifetime consumption of maize, black beans, kidney beans, groundnuts and chili pepper contaminated with aldrin, dieldrin, endrin, HCB, heptachlor, o,p'-DDT, p,p'-DDD, p,p'-DDT, p,p'-DDE and β-HCH, could pose health risks. (4) Conclusion: These results show that there is an urgent need of pesticide usage regulation, effective application of pesticide bans and management of obsolete pesticide stocks in Cameroon.
Keywords: Cameroon; POPs; food safety; organochlorine; pesticide residues; risk assessment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Organochlorine pesticide residues in dairy products in Jordan.Chemosphere. 2009 Oct;77(5):673-8. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.07.045. Epub 2009 Aug 19. Chemosphere. 2009. PMID: 19695668
-
Concentrations and potential health hazards of organochlorine pesticides in (shallow) groundwater of Taihu Lake region, China.Sci Total Environ. 2014 Feb 1;470-471:1047-55. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.10.056. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Sci Total Environ. 2014. PMID: 24239826
-
Evaluation of 99 Pesticide Residues in Major Agricultural Products from the Western Highlands Zone of Cameroon Using QuEChERS Method Extraction and LC-MS/MS and GC-ECD Analyses.Foods. 2018 Nov 7;7(11):184. doi: 10.3390/foods7110184. Foods. 2018. PMID: 30405079 Free PMC article.
-
Organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in foodstuffs from Asian and oceanic countries.Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 1997;152:1-55. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4612-1964-4_1. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 1997. PMID: 9297984 Review.
-
Pesticides in the hydrogeo-environment: a review of contaminant prevalence, source and mobilisation in India.Environ Geochem Health. 2023 Aug;45(8):5481-5513. doi: 10.1007/s10653-023-01608-6. Epub 2023 May 15. Environ Geochem Health. 2023. PMID: 37183216 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dietary risk assessment of drinking water and fish from cultivated wetlands of Ndop.J Water Health. 2024 Jun;22(6):1075-1087. doi: 10.2166/wh.2024.057. Epub 2024 May 28. J Water Health. 2024. PMID: 38935458
-
Health risk assessment of potassium bromate in bread in Ghana.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 17;10(2):e24519. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24519. eCollection 2024 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39734470 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions to Reduce Pesticide Exposure from the Agricultural Sector in Africa: A Workshop Report.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Jul 23;19(15):8973. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19158973. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35897345 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Review of Pesticide Residues in Peppers.Foods. 2023 Feb 24;12(5):970. doi: 10.3390/foods12050970. Foods. 2023. PMID: 36900487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potassium bromate in bread, health risks to bread consumers and toxicity symptoms amongst bakers in Bamenda, North West Region of Cameroon.Heliyon. 2023 Jan 21;9(2):e13146. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13146. eCollection 2023 Feb. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 36747561 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gerber R., Smit N.J., Van Vuren J.H.J., Nakayama S.M.M., Yohannes Y.B., Ikenaka Y., Ishizuka M., Wepener V. Bioaccumulation and human health risk assessment of DDT and other organochlorine pesticides in an apex aquatic predator from a premier conservation area. Sci. Total Environ. 2016;550:522–533. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.01.129. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

